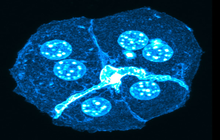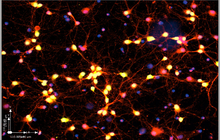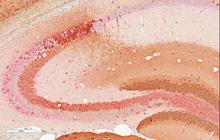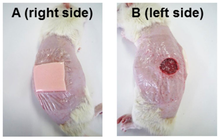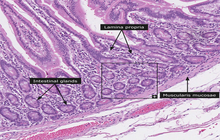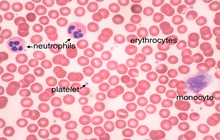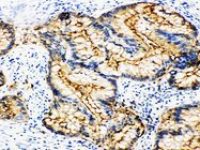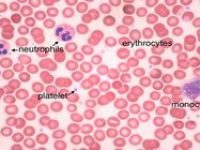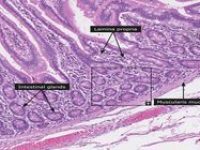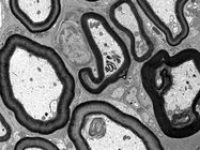
Histological services, tissue engineering and pathology staining
- Preparation of paraffin and frozen tissue sections in different sizes
- General and specialized tissue and cell staining
- Immunocytochemistry (ICC) technique
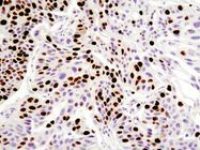
- Immunohistochemistry (IHC) technique
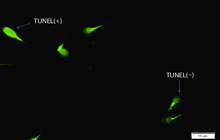
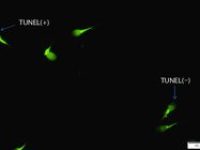
- Perform tunnel technique to evaluate apoptosis
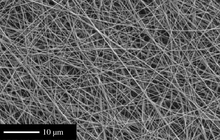
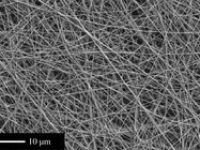
- Preparation of sections from chemical and natural tissue scaffolds
- Prepare educational slides for students from all available tissues
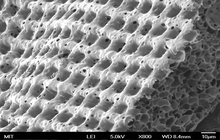
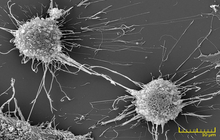
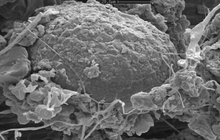
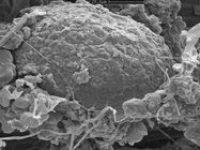
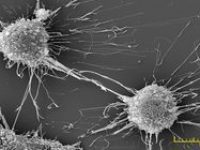
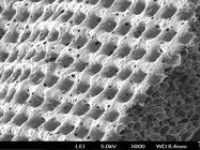
- Examination of cell placement on tissue scaffolds with SEM microscopy
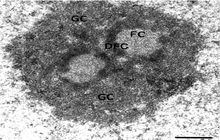
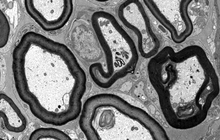
- Preparation of tissue sections for examination with a TEM microscope
Histological methods includes sample processing in the pathology laboratory, preparation of the slide and its examination under a microscope, sample fixation, molding, microtome cutting, staining and assembly of the slides.
On the other hand, in cutting-edge sciences such as tissue engineering, the use of up-to-date techniques for section preparation and cell tracking and engineered tissue structure has contributed significantly to the development of new studies.
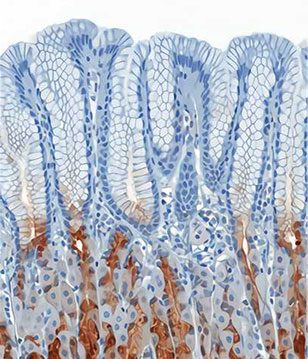
Complete introduction of histological services
Preparation of paraffin and frozen tissue sections
Tissues can be store for long periods of time through paraffin molding and freezing. In Histogenotech samples are molded after tissue dehydration by paraffin dispenser. Also microtome cutting machine is use for tissue preparation for various staining.
Immunocytochemical technique
Immunocytochemistry is a common technique to detect specific proteins or antigens in cells using a variety of antibodies. Histogenotech is ready to provide immunocytochemical services for researchers due to stored antibody bank and existence of light and fluorescent microscopes in laboratory.
Immunohistochemical technique
This technique is used to study the expression of a variety of proteins in different tissue. Histogenotech and his trained specialist are ready to provide immunohistochemical services for professors, students and researchers with a bank of antibodies and specific histological dyes.
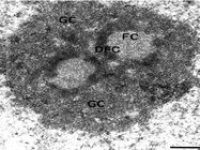
Examination of apoptosis (tunnel)
The SEM microscope is perform to study the morphology of nanostructures and to identify compounds as well as to accurately examine the cell surface. To complement its histological and cellular services, Histogenotech has also put on its agenda the evaluation of chemical composition gradients, breakdown stages and the identification of compounds on the surface of samples.
Preparation of tissue scaffolds
Structural examination of tissues and cells plays a crucial role in advancing new studies at Histogenotech histological unit because in modern research, the morphology of cells and organs is examined by TEM micrograph.
Evaluation of the cells on the scaffold
The SEM microscope is perform to study the morphology of nanostructures and to identify compounds as well as to accurately examine the cell surface. To complement its histological and cellular services, Histogenotech has also put on its agenda the evaluation of chemical composition gradients, breakdown stages and the identification of compounds on the surface of samples.
Preparation of tissue sections for examination with a TEM microscope
Structural examination of tissues and cells plays a crucial role in advancing new studies at Histogenotech histological unit because in modern research, the morphology of cells and organs is examined by TEM micrograph.
Preparation of training slides
Histogenotech in order to improve the scientific level of students and also to facilitate the educational process for university attends in the fields of histology, embryology, hematology, cellular and molecular, has prepared educational slides from all tissues and organs of the body.
The basis of Mason trichrome staining is the identification of collagen filaments that appear in blue. Also, the keratin contents of cutaneous tissue within the cytoplasm of epithelial cells are also seen in this type of staining.
Alcian blue staining is one of the most exclusive methods for displaying bone formation centers during the fetal period. This dye is also considered a specific staining of mast cells. As a result of this staining, the muco-polysaccharide turns blue to dark blue, and the nuclei turn pink.
Chrysalis violet is an effective and reliable staining. Chrysalis violet is used to stain Heinz bodies in red blood cells or stain brain and spinal cord neurons. It is also used to detect Nissl bodies in the cytoplasm of nerve cells in paraformaldehyde or formalin-fixed tissues. Nissl bodies will be painted blue-purple with Chrysalis violet staining. This staining is commonly used to identify the main structure of nerve cells in brain and spinal cord tissue.
This staining method is used for staining axons and myelin in paraffin, formalin and frozen tissue samples. Also, this staining is used to examine nerve structures in the tissue sections of the brain or spinal cord.
Giemsa is used for karyotyping (G-banding) chromosomes staining. Giemsa is also used as a classic staining for examining blood smear slices and bone marrow samples.
Sudan black is used to stain various types of lipids such as phospholipids, sterols and neutral triglycerides. Sudan Black, like other Sudan dyes, is not specific to fats and can be used to stain chromosomes, Golgi apparatus and leukocyte granules.
Acridine Orange is a fluorescent dye with the capacity of penetrating to the cell nucleus and binding to nucleic acids, emitting a green fluorescent dye when bound to dsDNA and a red fluorescent dye when bound to ssDNA or RNA which make Acridine Orange suitable for cell cycle studies. Acridine orange is also used to stain lysosomes.
Jones dye is used in staining basement membranes and is also widely used in the study of various layers of kidney tissue.
This staining is used to study the morphology of neurons and make nerve cells dark. In this staining, different parts of the neuron, such as dendrites, dendritic spines and axons can be examined.
Verhoefe is used to stain the elastic tissues in the blood vessels, cartilage, lungs, skin, bladder and some different ligaments.
Feulgen dye is used to stain DNA in tissue sections and cells. It is a common staining technique for DNA observation in histology which selectively stains DNA.
Toluidine blue is often used to identify mast cells due to the presence of heparin in their cytoplasmic granules. It is also used to stain proteoglycans and glycosaminoglycan in tissues such as cartilage.
Types of staining methods
1. Masson’s trichrome staining
The basis of Mason trichrome staining is the identification of collagen filaments that appear in blue. Also, the keratin contents of cutaneous tissue within the cytoplasm of epithelial cells are also seen in this type of staining.
2. Alcian blue staining
Alcian blue staining is one of the most exclusive methods for displaying bone formation centers during the fetal period. This dye is also considered a specific staining of mast cells. As a result of this staining, the muco-polysaccharide turns blue to dark blue, and the nuclei turn pink.
3. Chrysalis violet staining
Chrysalis violet is an effective and reliable staining. Chrysalis violet is used to stain Heinz bodies in red blood cells or stain brain and spinal cord neurons. It is also used to detect Nissl bodies in the cytoplasm of nerve cells in paraformaldehyde or formalin-fixed tissues. Nissl bodies will be painted blue-purple with Chrysalis violet staining. This staining is commonly used to identify the main structure of nerve cells in brain and spinal cord tissue.
4. Luxol Fast Blue stainingg
This staining method is used for staining axons and myelin in paraffin, formalin and frozen tissue samples. Also, this staining is used to examine nerve structures in the tissue sections of the brain or spinal cord.
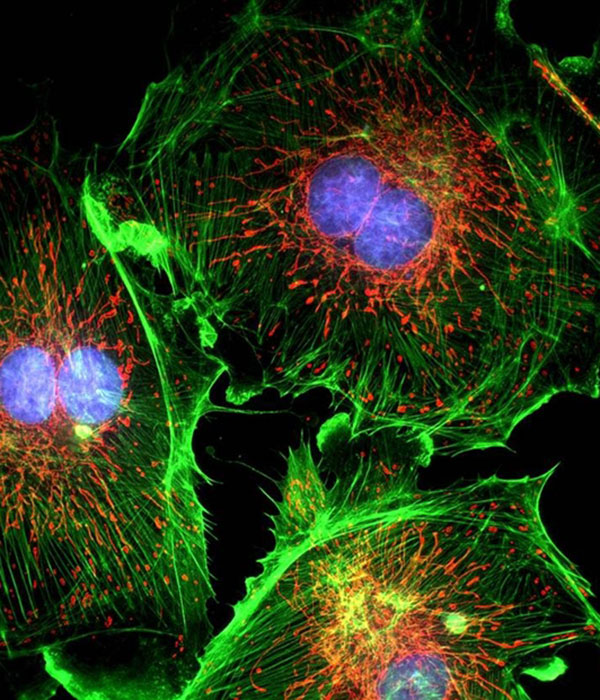







5. Reticulin staining
Reticulin is used to identify reticular fibers, proteins and nucleic acids. In addition, this compound is used to identify proteins on the SDS page. Other applications include the preparation of samples for SEM microscopy. Reticulin also has antiseptic properties which are used in medical cases.
6. Periodic acid shift dye (PAS)
PAS dye stains glycogen and carbohydrate and also used to characterize basement membranes. Thus, the periodic acid oxidizes the hydroxyl glycogen to form a di-aldehyde, which produces a red color with the Schiff reagent. PAS staining can stain all sort of polysaccharides in sample.
7. Oil Red staining
Transgenic animals have become key tools in genomic studies and the development of human disease models for the study of new drugs. Transgenic models involve adding external genetic information to the animal genome or inhibiting the expression of a specific gene in the animal’s body.8. Alizarin Red staining
Alizarin Red staining is used for calcium detection in tissue sections and cultured cells. Alizarin red is also used to identify calcium-containing osteocytes in the differential culture of human and rodent mesenchymal stem cells.
9. Giemsa staining
Giemsa is used for karyotyping (G-banding) chromosomes staining. Giemsa is also used as a classic staining for examining blood smear slices and bone marrow samples.
10. Sudan Black Staining (Black Sudan)
Sudan black is used to stain various types of lipids such as phospholipids, sterols and neutral triglycerides. Sudan Black, like other Sudan dyes, is not specific to fats and can be used to stain chromosomes, Golgi apparatus and leukocyte granules.
11. Acridine Orange staining
Acridine Orange is a fluorescent dye with the capacity of penetrating to the cell nucleus and binding to nucleic acids, emitting a green fluorescent dye when bound to dsDNA and a red fluorescent dye when bound to ssDNA or RNA which make Acridine Orange suitable for cell cycle studies. Acridine orange is also used to stain lysosomes.
12. Jones staining
Jones dye is used in staining basement membranes and is also widely used in the study of various layers of kidney tissue.








13. Golgi staining
This staining is used to study the morphology of neurons and make nerve cells dark. In this staining, different parts of the neuron, such as dendrites, dendritic spines and axons can be examined.
14. Verhoeff staining
Verhoefe is used to stain the elastic tissues in the blood vessels, cartilage, lungs, skin, bladder and some different ligaments.
15. Feulgen staining
Feulgen dye is used to stain DNA in tissue sections and cells. It is a common staining technique for DNA observation in histology which selectively stains DNA.
16. Toluidine blue staining
Toluidine blue is often used to identify mast cells due to the presence of heparin in their cytoplasmic granules. It is also used to stain proteoglycans and glycosaminoglycan in tissues such as cartilage.
17. Orcein staining
Like Werhaf dye, it is used to stain the elastic tissues in the blood vessels and cartilage. Orcein staining is used for sex chromatin staining and some nuclear staining.
18. Light Green staining
Light green or light green stain is mainly used in pathology and cytology examinations. Light green is a differential dye in Mason trichrome staining that is used to identify collagen fibers.
19. Trypan Blue staining
Trypan blue is an impermeable dye used to estimate the number of dead cells in a cell population. The basis of this staining is based on the fact that this dye is impermeable and cannot enter the cell as long as the cell is alive unless the cell membrane is damaged.
20. Pap smear staining
Pap smear, or Pap test, is a test to detect abnormal cells in the cervix which may be cancerous. It should be noted that some microbial, fungal and viral infections of the uterus can also be examined I n this type of staining.




You may find the answer to your question
Frequently Asked Questions
In order to fix the deeper parts of the tissue, the thickness of the tissue should be a maximum of 0.5 cm, while the length and width of the tissue can be up to one centimeter.
Fixatives include alcohols, picric-formaldehyde acid, paraformaldehyde, formalin, and Bouin solution, with 4% paraformaldehyde commonly used for cells and 10% formalin for tissues. Of course, Bouin is used for some tissues and alcohol is used for some smears. The volume of fixative agent is depemd on content of blood, depending on the size of the tissue and the amount of blood inside the tissue, up to three times of the fixed tissue should be placed on the sample.
The temperature of 4 °C is suitable for keeping the fixed cell and 22 to 25 °C is suitable for the fixed tissue.
For the different tests including, immunocytochemistry, flow cytometry, cell tunneling, immunofluorescence, immunohistochemistry, tissue tunneling, general and specialized tissue staining samples should be fix. For cell cycle tests, cell survival tests, apoptosis, molecular techniques by PCR, protein testing techniques such as western blotting and ELISA, and antioxidant tests in cells and tissues should not be fixed.
Some slides which are stained with hematoxylin dye, can de-stain with decolorizer and used for re-staining.
These samples cannot be used in most cases. However in some cases, after examining a tissue sample, the health of the tissue can be ensured. In general, this is possible in tissues with less water.
Pathological images and qualitative results obtained in laboratory can be presented quantitatively and graphically with Image J software.
In general staining, abnormal or deformed parts can be detected according to the normal characteristics of each texture that can be seen in the images.
In general staining, general tissue structures are observed, but in specialized staining, an organelle or tissue string or a specific part of a cell or tissue is visible.
Usually, several staining methods should be used to evaluate a study, but in some studies, a single test can yield multiple results.
These two methods are for examining a specific marker or protein in a tissue or cell. However dye at the end of the immunohistochemistry method is DAB, which can be seen with a light microscope, but in immunofluorescence, the dye is FITC or PE or other dyes which should be examined with a fluorescence microscope.
The sample must be fixed like other tissues. First, in order to make the tissue soft, calcium salts must be removed, which is called decalcification that can perform using 5% nitric acid for one to 4 days. The acid is then neutralized with 5% sodium sulfate.