Providing molecular services with the most advanced devices and the most experienced staffs
Some of our services in Histogenotech
- Extraction of RNA from tissues and cells by manual and commercial methods
- cDNA synthesis
- Methods of extracting genomic DNA from blood, saliva with manual and commercial methods
- Primer design for gene detection
- Primer design for micro RNA testing
- Design expressive vectors
- Perform Real-time PCR technique
- Primer design for noncoding RNAs (microRNA, LncRNA)
- Design expressive vectors
- Perform Multiplex PCR technique
- Investigation of methylation in the genome by BSP and MSP methods
- Evaluation of polymorphism and gene mutation by RFLP, Nested PCR, ARMS and genome sequencing
- Investigation of telomere length using quantitative PCR method
- Investigation of histone variants and acetylation
One of the most important field in molecular biology is the inference and interaction between intracellular systems (including RNA, DNA, and protein-building interactions) and their regulation mechanisms.
Advances in molecular biology over the past two decades have enhanced the efficiency and evolution of DNA-dependent experiments in the medical sciences.

Molecular Studies Services
Extraction of RNA from tissues and cells with manual and commercial methods
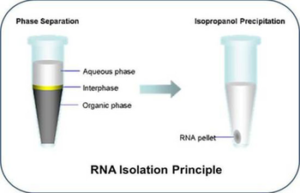
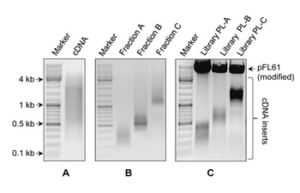
Extraction of RNA from biological samples is the first fundamental step in the study of many biological processes. RNA plays a key role in gene expression and regulation. The process of RNA extraction for gene expression begins with homogenization of the sample and then cell lysis to release RNA, followed by washing and purification of salts and other contaminants using a high-speed centrifuge. Histogenotech is able to extract total RNA and specific types of RNA (microRNA) by two methods (phenol chloroform (Trizol)) and commercial kits from different biological samples (cells, oocytes, hard and soft tissues, plant tissues, etc.) with maximum concentration and quality. Nanodrop assay use in order to confirm the quality of extracted RNA. Also, its purity percentage and concentration will be controlled and ready to be used to study gene expression, total genome sequencing (NGS) and other molecular studies.
CDNA synthesis
To study the genes expression of biological samples, it is necessary to determine the copy numbers of targeted genes at the mRNA level. On the other hand, the basis of PCR process for gene expression is DNA replication. Therefore, it is necessary to first convert RNA to DNA using reverse transcription enzyme, which is called cDNA (Complementry DNA). The reverse transcription reaction (cDNA synthesis) can be performed on whole cytoplasmic RNA or on mRNA. In Histogenotech, cDNA synthesis is performed using single-stage or multi-stage commercial kits with general primers (Random hexamer-Oligo dT) or each gene specific primers (microRNA stem loop) in a regular temperature cycle which is proved by a thermocycler.


Methods of extracting genomic DNA from blood, saliva with manual and commercial methods
DNA extraction is often a first step in many diagnostic processes used to detect a variety of bacteria, viruses in the environment, as well as to diagnose diseases and genetic disorders. DNA extraction involves the lysis of cells and the dissolution of DNA, which can perform by chemical or enzymatic methods to remove macromolecules, lipids, RNA, or proteins. Common techniques for DNA extraction are organic extraction (phenol-chloroform method), inorganic method (desalination and proteinase K treatment) and adsorption method (silica gel membrane). In Histogenotech, using manual methods as well as existing commercial kits, DNA is extracted from various tissues, including blood, body fluids, tissues embedded in paraffin or formalin, frozen tissues, and ancient specimens, and so on.
Plasmid amplification, extraction and purification
The rapid increase in antibiotic resistance has led to further studies on mobile genetic elements (such as plasmids). Plasmids are the major carriers of gene sharing among bacteria. Therefore, they play a key role in microbial evolution and the development of antibiotic resistance. So, studies on plasmids are very important among different animal and human species due to the increase in antibiotic resistance in pathogenic bacteria. Because the plasmid contains a small portion of the total DNA, its extraction requires the process of bacterial multiplication in an incubator and then purification. In Histogenotech, plasmid replication, extraction and purification processes can be performed using specialized commercial kits as well as manual methods.
Primer design for gene expression studies
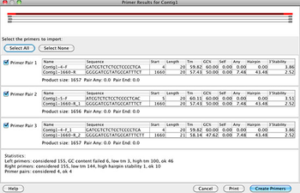
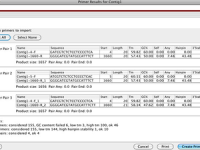
Primer structure is made from oligo-deoxy nucleotides, or single-stranded DNA, that are able to bind specifically to a specific region of target DNA. After primer hybridization in the complement region, DNA synthesis continues from the OH end of the primer. Conscious primer design is at the heart of any research project. A non-suitable primer will result in a non-proprietary product and ultimately non-speciefic results, a variety of web-based software has been developed to minimize errors in the primer design process. In Histogenotech, using the technical knowledge of experienced staffs, there are different types of primers like exon-exon junction, intron-spanning and others to study gene expression by cyber-green and classical methods. After designing the primer, the quality of the primers will be controlled using common software (Primer3, UCSC, Gene Runner, Oligo7, Primer Blast), then the primer will be synthesized. Efficiency of our designed primers in the laboratory examine by serial dilution and drawing a standard curve and also controlling the size of the resulting products using gel electrophoresis.
Perform PCR test technique on gel electrophoresis
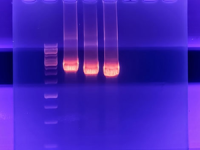
Investigation of gene expression by classical PCR method is one of the most widely used methods for gene expression analysis in which PCR product is evaluated using agarose gel electrophoresis. The advantage of this method over qPCR is the examination of DNA products based on size. Agarose gel electrophoresis is the simplest method for the analysis of PCR products. In this method, the size of the PCR product is measured using a ladder. In Histogenotech, this method is used to examine gene expression, detecting bacterial strains, viruses, mutant species, and so on. The PCR products after electrophoresis are placed in a transluminator or gel documentation with UV light and the bands in terms of density and size can be observe. Also, the images are evaluated and analyzed using Image j software for quantity results.
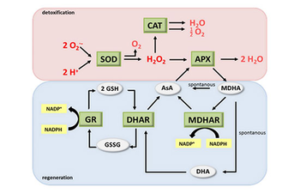
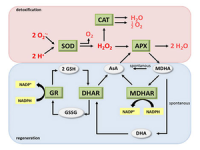
Evaluation of oxidative stress and evaluation of cell and tissue antioxidants by ELISA method (SOD, MDA, GPX, CAT, GSH, PC)
Oxidative stress An imbalance between oxidant and antioxidant molecules is in favor of oxidants that cause aging and disease. Antioxidants or antioxidants, by binding to stressors, reduce the effects of dangerous oxidants and reduce their destructive power. For this reason, measuring the amount of antioxidants is so valuable that these compounds are evaluated in histogenotech using special kits. For example, the measurement of superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), glutathione peroxidase (GPX) as well as some antioxidants (such as GSH) are examined non-enzymatically using chemical compounds in this center. Damage caused by stressors can be examined at three levels: 1- Protein damage, 2- Damage to fat metabolism 3- Damage to DNA. Carbonyl protein (PC) content is a common marker for protein level damage. Peroxidation of lipids (fatty acids) is usually the main indicator of ROS-induced damage to cell membranes by measuring malondialdehyde (MDA) levels as one of the end products of unsaturated fatty acid peroxidation.
One of the most important tests to evaluate the susceptibility and antibiotic resistance of pathogenic bacteria as well as antimicrobial effects of nanoparticles, plant extracts and various scaffolds, Use of antibiotic susceptibility and resistance tests based on diffusion in the environment. Histogenotech microbiology laboratory due to the benefit of its rich antibiotic bank Perform all these tests for researchers.
In many tests to check antibiotic resistance and sensitivity, it is important to obtain a resistance threshold and to accurately assess the concentration of bactericidal. Therefore, dilution tests are important. The Histogenotech Microbiology Laboratory, with its experienced specialists, is ready to provide services and perform MIC and MBC tests for researchers.
Biofilm formation in microbial populations in infection is like a disaster. The importance of bacterial biofilm structures in nosocomial infections and antibiotic resistance needs to be examined more closely. In Histogenotech microbiology unit, biofilm is measured by microplate plate (MTP) method using crystal violet in phenotypic terms. Also, the existence and expression of genes involved in biofilm production is provided for researchers and students in this laboratory.
In the Histogenotech microbiology laboratory, all tests related to biochemical analysis (fermentation of sugars, study of enzymes, study of metabolic pathways and evaluation of sensitivity and resistance to chemicals), Serological examination (use of antigen and antibody reactions in different methods in the diagnosis of microorganisms) As well as the study of molecular tests to detect slow-growing and hard-growing organisms and the contamination of various materials such as contaminated cell culture media and…. Done.
Investigation of microbial contamination in different water and food samples in industry and their environment and also, the origin of various infections and diseases needs to be investigated which can be done in two ways: microbial (culture of microorganisms) and molecular for different types of microorganisms. At the Histogenotech Microbiology Laboratory, we are ready to serve researchers in the field using rich microbial banks as well as advanced research equipment.
The production of enzymes and various substances by microorganisms due to their physiological and genetic characteristics has long been of interest to many researchers in biotechnology, pharmacy and industrial microbiology. In response to this important and to meet the needs of researchers in this field, another service of Histogenotech microbial laboratory is plasmid isolation and purification, expression vector design and cloning in different hosts.
Probiotics are a microbial population of normal human body flora that can be used to supplement the microbial population of the human body. Today, the importance of probiotics in the prevention of diseases such as autoimmune diseases, skin diseases, cancer, Covid-19 disease, as well as the importance of probiotics in various industries such as livestock and poultry has been identified. Histogenotech, with the help of efficient specialists and up-to-date technology, has provided probiotic isolation, purification and identification services for students and researchers.
Noncoding RNA (lncRNA and microRNA)
lncRNA has been implicated in a number of biological processes and in the pathophysiology of human disease in recent years. miRNAs and lncRNAs, as non-coding RNAs, are key regulators of gene expression networks that control a variety of biological processes, including proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, metabolism, and pathogen interactions. Due to the growing importance of miRNAs in numerous biological mechanisms, several qPCR-based methods have been developed for analyzing miRNA expression in recent years. Primer design for miRNA RT-qPCR is a major challenge due to its short length (mean 22 nucleotides).Design expressive vectors
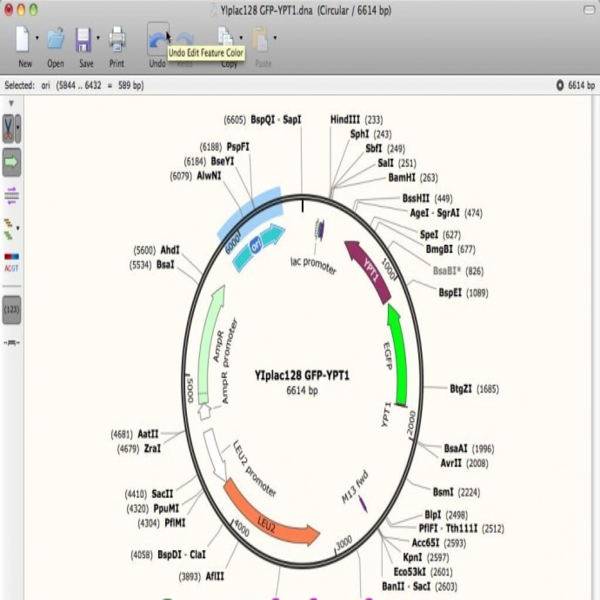
The process of cloning is to transfer a gene which is carried out by a vector (expression vector) to the host cell, followed by proliferation and increased protein expression. The importance of the cloning process in achieving a high volume of a particular type of pure protein that it is very important in the pharmaceutical industry and the production of recombinant proteins. In addition, scientists have been able to understand the physiology, molecular mechanisms, and patterns of gene expression in cells and organisms through the increasing development of molecular cloning strategies. In order to design a suitable vector as a carrier of a gene in a host cell, it is necessary to design the desired DNA fragment so that there is a cut-off site at both ends for the desired cleavage enzymes. In Histogenotech, expressive vector design is perform using special software (Snapgene) to control cutting sites, genome sequences and vector-related features, and the confirmation of process of cloning and screening of recombinant colonies are evaluated using staining and finally PCR.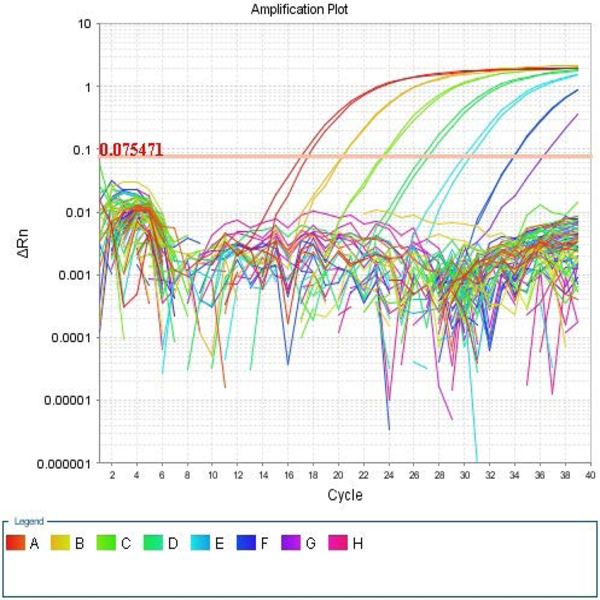
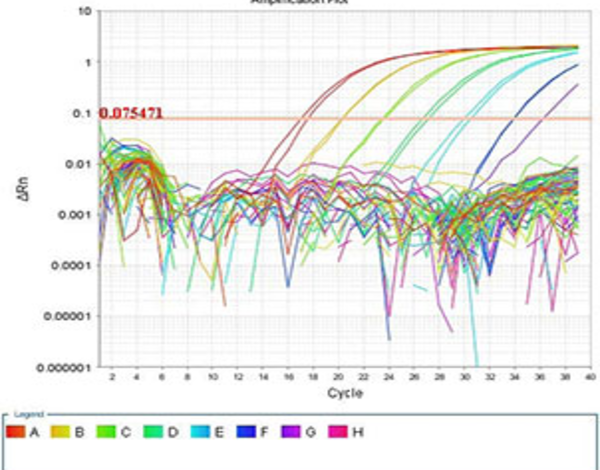
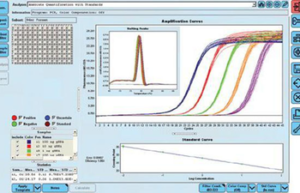
Performing Real-time PCR technique
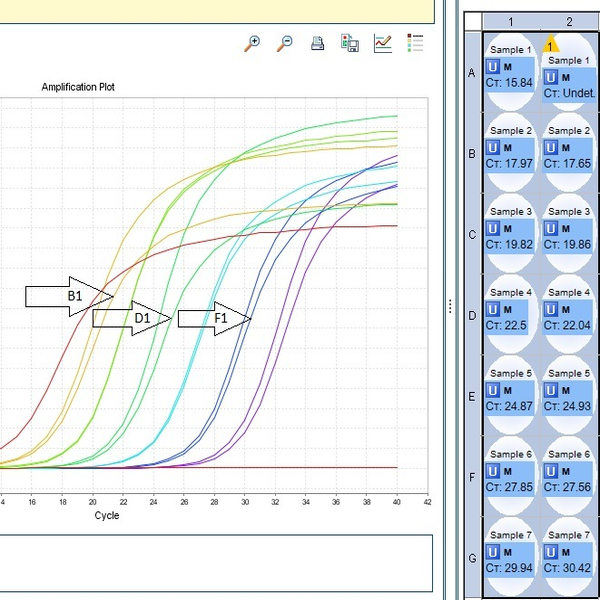
The real-time PCR method is a combination of classic PCR with the chemistry-physics properties of fluorescent materials, which uses a digital device to measure the amount of fluorescent changes in the samples being measured. This method has the ability to quantitatively measure copies of the template (cDNA, DNA). qPCR is widely used in diagnostic tests for the rapid diagnosis of cancers, genetic abnormalities, and infectious diseases such as new strains of influenza and coronavirus. In Histogenotech, the expression of various genes using ABI thermocycler device, Step one model, and single-stage or multi-stage commercial kits has been used continuously in various research projects, and the obtained results are reported after normalization with reference genes expressions level (relative change).Perform Multiplex PCR technique
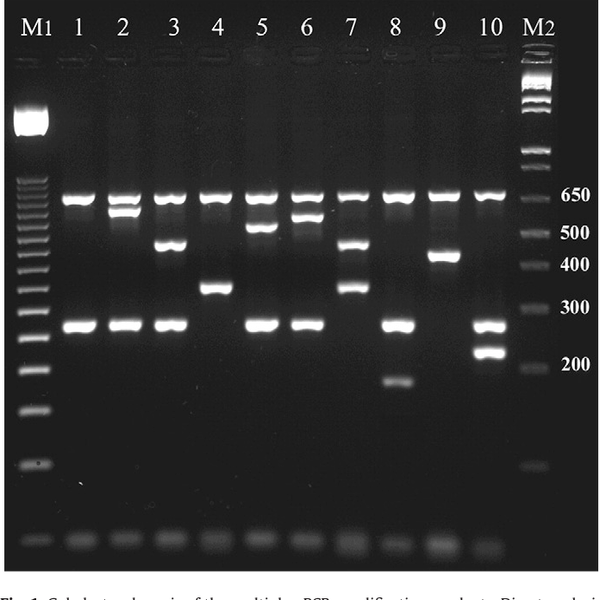
Multiplex PCR is a type of PCR in which two or more target sites in a PCR reaction are evaluated. For this purpose, specific primers of each sequence with different sizes will be designed and separated by gel electrophoresis. In this method, two or more factors can be identified that is time and cost benefit. Primer designing is very important for this type of PCR, which is perform in Histogenotech using common software in this field (PrimerPlex and…). Using these primer design softwares, the mismatch of Tm primers is checked and minimized. In this set, multiplex PCR is used in various research projects, including in microbial genetics, pathogen identification and microbial detection, and detection of purity percentage of livestock products.Investigation of methylation in the genome by BSP and MSP methods
In epigenetic changes unlike inherited genetic changes, there is no change in DNA sequence. Although almost all living cells contain the same genetic information, not all genes are expressed at the same time. DNA methylation is catalyzed by a family of DNA methyltransferases (Dnmts). Genetic research on DNA methylation can provide important information about the underlying processes that normally help determine cell function. One of the most common methods for determining the state of methylation in DNA sequences is DNA treatment with bisulfite, which causes the non-methylated cytosine bases to lose their amine group and become the uracil base. Using different experiences in this field, Histogenotech investigates methylation using two methods of MSP (methylation-specific PCR and BSP (bisulfite sequencing PCR), using specific primers.Evaluation of polymorphism and gene mutation by RFLP, Nested PCR, ARMS and genome sequencing
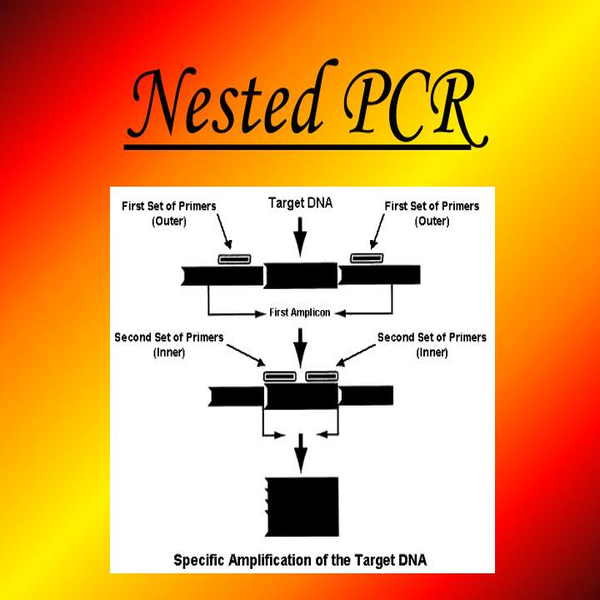
Simultaneous occurrence of two or more discontinuous genotypes or alleles in a population is called genetic polymorphism. The study of gene polymorphisms provides a new context for the study of the pathogenesis and progression of diseases and the nature of phenotypic diversity in which, in addition to the genetic causes of disorders, DNA changes, disease susceptibility, or treatment options can be identified. A wide range of methods are used to detect mutations, including the type of nucleic acid (DNA or RNA), the type of sample (blood, tissue, etc.) and the number of mutations that influence the choice of method. In Histogenotech with RFLP technique, point mutations that result in restriction sequence and site of cleavage by finite-acting endonucleases are identified using specific cleavage enzymes. In addition, using the ARMS-PCR technique of point mutations, the genotype (normal, heterozygous and homozygous) is a determinable specimen. In cases where a general analysis of a small part of the genome sequence is required, Sanger sequencing will be used.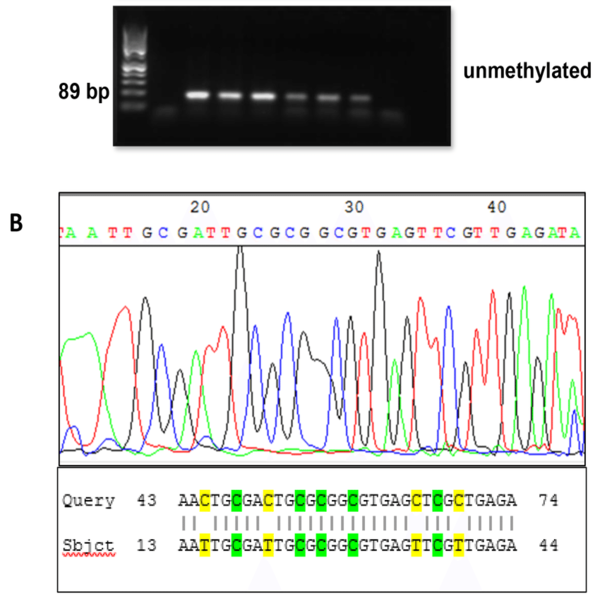
Investigation of telomere length using quantitative PCR method
Telomeres are sequential and duplicate arrays of TTAGGGn at the end of all linear chromosomes that play a protective role at the end of the chromosome by forming special telomere structures called T-rings. In many types of human somatic cells there is little telomerase activity, which leads to telomere loss. Gradual telomere shortening can also lead to aging and genetic disorders affecting telomeres (telomere) such as age-related diseases such as infertility, Arthritis, diabetes, cancer, cardiovascular and neurological diseases. Its identification will assist in age-related genetic pathologies in humans. In Histogenotech, telomere length is studied, in addition to measuring the expression of effective proteins in this field (TERT-TRF) by measuring it at the DNA level using quantitative PCR. In this method, the number of duplicate copies of the telomere (T) is calculated as the number of copies of the single copy gene (T / S ratio).Investigation of histone variants and acetylation
Chromatin, as the physiological pattern of eukaryotic genetic information, is associated with a variety of post-translational changes. Histones are the nucleus-forming molecules that provide an octameric structure for DNA packaging in eukaryotes. Histone variants play a key role in diversifying the structure of chromatin. Researchers believe that many common multifactorial diseases, such as diabetes, Alzheimer’s and other diseases, are not inherited alone, and that it is environmental (epigenetic) changes at the DNA and histone levels that can affect the expression of genes involved in these disorders. Changes after translation of the amino terminals of histones in one can cause transcription and in others can prevent it. Numerous environmental factors can exert their influence by causing acetylation, phosphorylation and methylation changes in histones. In histogenetics, epigenetic changes for acetylation, methylation and identification of histone variants are performed by quantitative expression of specific genes in this field.You may find the answer to your question
Frequently Asked Questions
The choice of PCR method is related to the design of the study. For example, quantitative PCR or classical PCR can be used to study gene expression at the mRNA and non-coding RNA levels. DNA is used to study genomic changes, gene mutations and polymorphisms, and the choice of PCR can be determined depending on the type of sample, the study method and the sensitivity of the study, the information contained in the gene bank, and so on. The ARMS method is used to detect point mutations in which the primer is designed exclusively based on different alleles. RFLP is used to detect the types of polymorphisms, genotypes, and screening for identified mutations based on differences in fragment size in enzymatic sections of PCR products. The Nested method is used to track the target DNA sequence, which uses two pairs of nested primers. The specificity of this method is very high due to the type of primer. In addition, PCR can be used to identify types of microbial strains, parasites, etc. For example, multiplex PCR has the ability to simultaneously identify several strains of bacteria or parasites in one reaction. In this test, several pairs of specific primers are used simultaneously.
One of the most common mistakes among students is using the term RT-PCR for three completely different tests, cDNA Synthesis, Real Time PCR and RT-PCR. In cDNA synthesis, RNA is used as a template to make the reverse transcriptase enzyme from DNA in a temperature cycle using a primer sequence (oligo dt or random hexamer) from DNA. In classical PCR and qPCR, cDNA is used as a template and will be amplified from a gene with a specific primer in several temperature cycles. The difference between the two PCRs is that qPCR uses a special thermocycler that can detect the reflected fluorescent signal and ultimately quantify the results. But in classical PCR, the results are reported semi-quantitatively, in which PCR products can be reported quantitatively after separation in gel electrophoresis with special software.
Freezers with a temperature of -80 °C are a good option for long-term storage of biological materials. This temperature prevents the breakdown of nucleic acids, proteins and many biological molecules. In cases where a temperature of -80 °C is not available or the conditions for sending the sample with dry ice are not possible, the samples can be immersed in aqueous sulfate salt solutions. A commercial, ready-to-use compound called RNALater is available that can be added to tissues isolated from an organism or cell. Solid tissues can be stored at RNALater at room temperature for one week. For long-term storage, samples containing this solution should be stored at -20 °C. To move and transfer frozen samples, it is necessary to maintain a negative temperature of -80 °C using industrial dry ice and transfer the samples to the desired laboratory immediately.
In the study of methylation, the basis of the performance of techniques based on biochemical changes by bisulfite is that non-methylated cytosine are converted to uracil with no modification on methylated cytosine. Therefore, depending on the presence or absence of methyl on cytosine, bisulfite causes special changes in DNA that can be evaluated by PCR, sequencing and microRNA methods. There are several methods available today to study DNA methylation analysis. However, no specific method is known as the “original” technique. Each method has advantages and disadvantages. Methods in which commercial kits can be used to detect methylation are known as the best methods for bisulfite treatment.
Depending on the technique, the quality required for the extracted RNA and DNA varies. High quality RNA is required in a variety of sequencing methods such as NGS, while a medium quality sample is sufficient for the PCTR real-time process. For this purpose, it is necessary to be informed about the quality of the extracted sample before doing the work. In the initial examination, the extracted sample is separated using 1.5% agarose gel. In a quality sample of DNA the corresponding band is seen on top of the gel. In RNA samples, 3 fragments of RNA, 18 S, 28 S, 5.8 S are separated into 3 separate bands. The presence of a smear in the gel indicates RNA degradation. In another method, a Bioanalyzer is used to accurately determine the quality of the extracted RNA, which is displayed as the RNA Value. In degraded RNA samples, the peak height for 28S and 18S rRNA peaks decreases, and in quality samples, peaks will be observed separately. The closer the RNA number is to 10, the higher the quality of the sample.
There are several software such as UCSC, Primer3, MEDUSA, Oligo7 for primer design, which has facilitated the primer design process for the user. After designing in Primer3 online software, primers should be checked on the Primer BLAST page on the NCBI website (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/tools/primer-blast) for checking specificity. In general, the following points should be considered in the design of primers: – Its length should be between 18 and 30 nucleotides, – It is better that the GC content is between 50% and 60% (increasing the amount of GC content leads to an increase The connection temperature will be followed by an increase in the strength of the hybrid and the primer dimmer) – There is no significant difference between the connection temperatures of the two leading and back primers (in optimal conditions this difference should be between negative 5 and 5) -Absence of complementary regions in a primer or different primers, especially at the end of 3 primers (to create a strong bond, the 3 ends must be one of the G or C nucleotides) – Tm primers should preferably be designed between 58-60 ° C and the maximum difference between Tm and two primers 3 degrees – Primer should be designed from stable regions (less likely to mutate) of target DNA Replication is done from cDNA that lacks introns, genomic DNA will not replicate.
One of the most important applications of Real-Time PCR is the quantification of gene expression, which is done in two ways, absolute and relative. The method of relative quantification is to determine the ratio of the number of mRNA copies and the expression of the desired gene. In this method, the number is not important and only the decrease or increase of gene expression is considered. Which compare this increase or decrease with a standard or reference gene. The basis of relative quantification is based on determining the ratio of expression of the desired gene to the reference gene. In this method, the PCR efficiency of both genes must be approximately equal, because otherwise the test result is associated with a high error. Then the difference between CT of both reference and reference genes is done) (2-CT in this case the normalization of the results is calculated based on the reference gene. Control group) show that it is necessary to differentiate DCT between control groups and other groups (2-CT) in which the control group will have the number 1 and other groups will show a number higher or lower than 1 Which indicate an increase or decrease in the expression of the desired gene.
The housekeeping gene is used to measure the relative expression of a gene without the need for a standard solution. An appropriate reference gene should have a stable expression among the samples and not be affected by various physiological changes. Reference genes are usually selected to normalize RT-qPCR data. Because these genes are involved in cellular basal metabolism, it is assumed that they are substantially expressed and are not affected by different treatments. However, reference genes may change due to changes in physiological conditions and tissue type, so for each study it is necessary to select the reference gene depending on the type of tissue and the type of study. In addition, it is recommended that at least two reference genes be used to ensure normalization of gene expression results. A reference gene should ideally be stable and used in target cells and tissues that do not show changes under normal or disease conditions. Reference genes used in various studies include 18sRNA, GAPDH, β-Actin, B2M.
Using the reading results in the nanodrop at a wavelength of 260-280 nm, the concentration and quality of RNA can be reported. In these results, the OD260 / OD280 ratio indicates the purity of the extracted RNA and is directly related to RNA contamination with the protein. Therefore, this proximity to the number 2 indicates that the protein is not contaminated. The OD260 / OD230 ratio is also used to evaluate the extent of RNA contamination to the materials used for extraction (phenols and salt compounds). The closer the value is to 2, the more favorable the conditions for the experiments.
RNA washing is the best way to remove salt contamination (OD260 / OD230 <1.8). If the RNA is extracted using trisol (phenol chloroform method), it is best to wash it with ethanol for desalination. In the method of using columns and commercial kits, by increasing the number of washes with ethanol, 70-80% of the amount of salts can be removed from the column. To remove high phenolics in the RNA sample, RNA can be dissolved in Tris-EDTA, a volume of chloroform added, and then centrifuged.
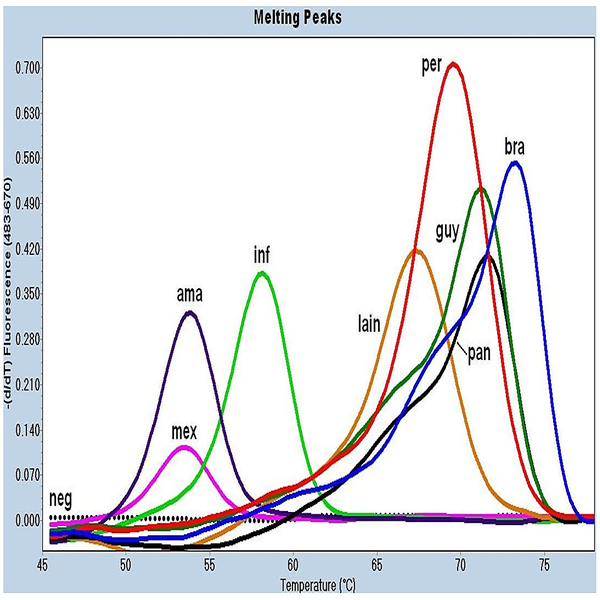
Existence of multiple peaks or additional bands in PCR results can have various reasons. In general, the presence of any peak or band indicates a product that has been amplified in the PCR process. In general, products with lower melting temperatures usually represent primer primers or proprietary products with short lengths. In gel electrophoresis, these products are located at the bottom of the gel. To remove these products, the primer must be designed more specifically and the connections between the primer pair and the dimer formation must be ensured. In some cases, this product can be removed by changing the annealing temperature or the primer connection temperature. In cases where the Tm of PCR products is high, the primer sequence may detect another fragment in the genome or the sample may be infected with another organism. In this case, in addition to being careful that the samples are not contaminated with other organisms, the primer can be replaced or in some cases, by changing the temperature, the proliferation of this product can be inhibited. In order to understand which of our products (which peaks) is specific, we must separate the products using gel electrophoresis and finally, depending on the size of the desired part for which the specific primer is designed, the specific product or Tm related to the target gene Specified.
In cases of decreasing RNA concentration, it is necessary to increase the amount of RNA deposition by using other compounds that increase the deposition process. To perform this process in the RNA precipitation step using alcohol, it is better to use concentrated isopropanol alcohol. At this stage, in addition to isoproponal, compounds of branched carbohydrates can help decrease RNA and increase deposition. In addition, lowering the temperature can lead to increased RNA deposition. For this reason, it is better to prolong the incubation process at 4 ° C after adding isopropanol.