Providing the latest and most up-to-date research services in the field of biotechnology
Some techniques performed in Histogenotech
- Design and product of vectors
- In vitro and in vivo Stem cell tracking with vectors
- Design and production of vectors containing microRNA and siRNA
- Perform CRISPR technique
- Performing bioinformatics services
- Perform microbial control tests to control the presence of microorganisms
- Extraction of antibiotics from fungi
- Isolation and identification of fungi for antibiotic production
- Preparation of bacterial and viral vectors
- Nano-particle biosynthesis by fungi and yeast
Biotechnology Studies Services
Design and product vectors
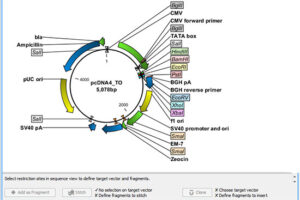
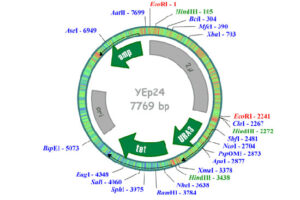
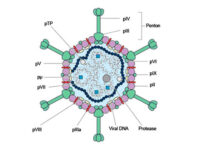
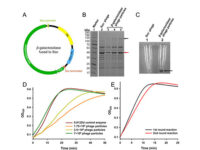
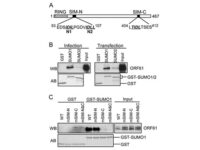
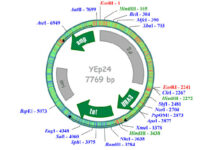
Vectors, or carriers of DNA fragments, are plasmids used in genetic engineering. Plasmids are small pieces of designed genetic material in a cell that multiply in the cytoplasm and independently of the chromosome and can alter cell function. These genomic fragments, with a molecular size of 1 to 1000 kPa, are often in the form of circular double-stranded DNA with an ori replication site from which plasmid replication begins.In the Histogenotech biotechnology department, these genetic components are designed in the form of vectors with the molecular basis of lentiviruses. Plasmids are found naturally in many bacteria, archaea, some fungi such as yeast and plants, but they can also be artificially transfected into animal cells. In the molecular section of the Histogenotech biotechnology laboratory, vectors are designed to detect stem and cancer cells. Due to the fact that Histogenotech microbial biotechnology laboratories are equipped with specialized centrifuges, it is possible to reproduce these vectors in high quantities.
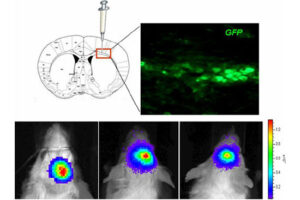
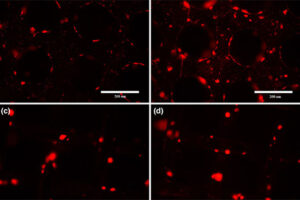
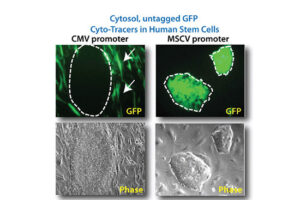
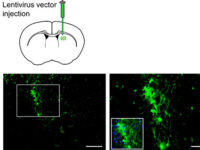
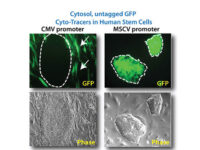
In vitro and In vivo Stem cell tracking with vectors
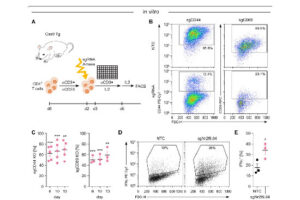
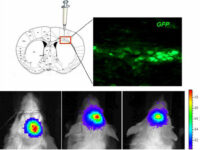
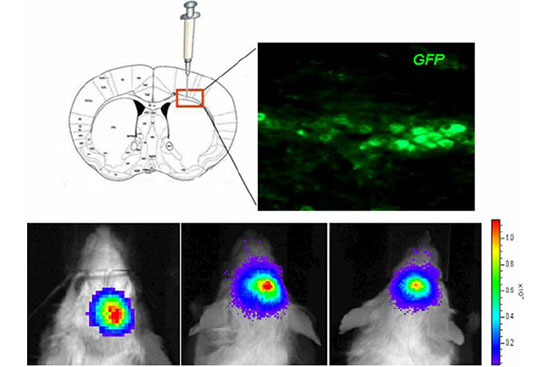
Vectors that carry the GFP tracer gene are used to detect stem cells in vitro. For this purpose, in the Histogenotech biotechnology laboratory, after preparing a susceptible or competitive bacterium containing a tracer fragment and antibiotic resistance gene, different strains of the bacterium are cultured and after amplifying the vector containing the tracer in the bacterium, the plasmids are purified using lipofectamine or electroporation is inserted into the stem cells. In the research and development department of Histogenotech Company, in order to carry out high-tech projects in doctoral and master’s degrees, various types of tracer vectors are designed and manufactured. In addition, in order to carry out knowledge-based projects or to produce high-tech products in the form of student research projects, these gene carriers are used to enter stem cells for in vitro and in vivo study. Due to the fact that Histogenotech cell and molecular laboratories are equipped with fluorescent microscopes, cell tracking can be done easily.
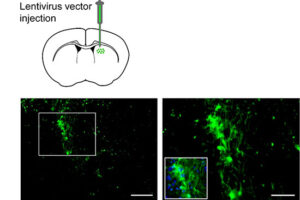
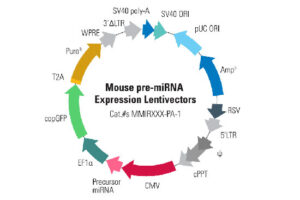
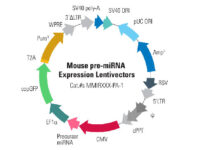
Design and fabrication of vectors containing microRNA and siRNA
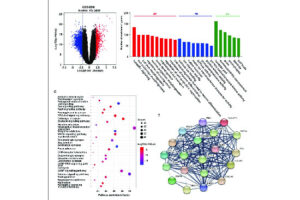
MicroRNAs are a group of small non-coding RNAs that are closely related to various diseases, including cancer. MicroRNAs regulate expression in eukaryotes by inhibiting translation or degradation of mRNA by partially pairing with the mRNA-terminal 3 (UTR′3) of the target gene. In Histogenotech cell and molecular laboratory, microRNA and siRNA are used in student projects and research projects of university professors due to the extensive implementation of various cellular techniques such as cell cycle regulation, cell growth, apoptosis, differentiation and stress response. Due to the potential of this group of 25-19 oligonucleotides to target a large number of mRNAs, for ISI articles to be published, or for patents and production in the field of biotechnology, many projects are being carried out in the Histogenotech Company. Using this group of small non-coding molecules, it can regulate molecular pathways and gene cascades, followed by over-express or down-regulate. Thus, due to the key role of these micromolecules in cellular-molecular processes, Histogenotech is ongoing providing free consulting services in the design or fabrication of efficient primers in the process of examining gene expression in the molecular laboratory.
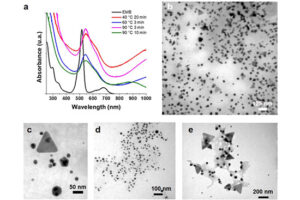
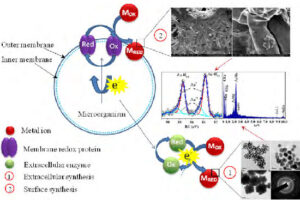
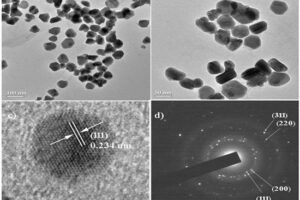
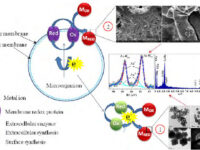
Nano-particle biosynthesis by fungi and yeast
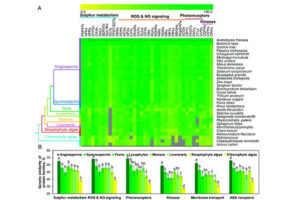
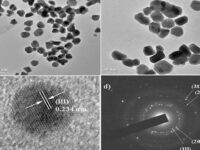
In order to perform the process of metabolism and other biological functions in microorganisms, the existing organic and mineral resources of the environment are consumed by these biological elements. These microorganisms are able to ingest metal ions in the environment or accumulate them in their organs. This accumulation leads to the production of different dimensions of particles in the form of nanoparticles. Acquisition of nanomaterials can create a special place in designing research projects, raising the scientific level of student articles and dissertations. Some magnetotactic bacteria are able to make magnetic nanoparticles. In addition, diatoms are able to use silicon materials and simple microorganisms to produce organic or inorganic compounds. In addition, during the process of culturing bacteria, fungi or yeast in the Histogenotech laboratory, new studies have been started on the production of nanoparticles from bacteria, fungi, algae and yeasts, which can produce interesting results for publication in authoritative articles for students and professors.
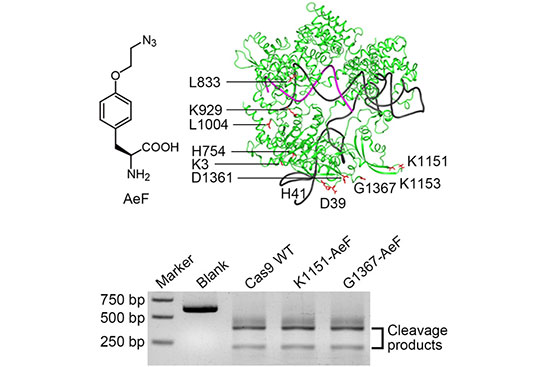
Perform CRISPR technique
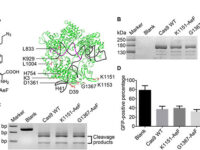
CRISPR-Cas9 technology for editing cell and tissue genomes has been considered by many researchers today. This advanced biotechnology technique is naturally derived from prokaryotes, with the goal of creating a defense barrier and immunization against viruses in bacteria. Inspired by this defense mechanism, the Crisper technique can inhibit, destroy, or inactivate the activity of genes in the cells of various living organisms. In this way, by cutting a piece of DNA or a gene, changes will occur in the cell genome, while the cell is alive and continuing to live. A variety of other Cas proteins can be used to inhibit, degrade, or inactivate genes, remove specific portions of genomic DNA, modify epigenomics, label DNA molecules, image chromosomes, and even edit RNA. Histogenotech intends to make extensive use of CRISPR for its scientific research. One of the valuable reasons for using crisper in research in various medical or environmental fields, especially in the agricultural and livestock industry, is its use in plant and animal genetic manipulations. This technique can also be used to kill pathogenic bacteria and viruses.
Performing bioinformatics services
Bioinformatics is for combining knowledge of statistics and biological concepts and analyzes and interprets biological information through mathematical and engineering calculations. In the case of computer analysis, a gene is inserted into a specific sequence and its protein structure or function is predicted. Due to the research activities of the Histogenotech in the design and formulation of chemical and herbal medicines, the analysis of the biological function of the active substance purified from medicinal plants or new medicinal formulations by bioinformatics methods is being carried out continuously. On the other hand, due to the study of gene cascade pathways in various research projects and the function of proteins controlling these pathways, the study of the role of different cellular receptors in the design of animal and preclinical studies seems necessary.
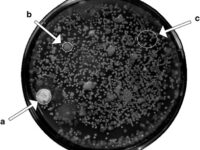
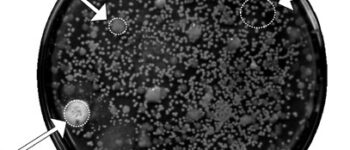
Perform microbial control tests to control the presence of microorganisms in the samples
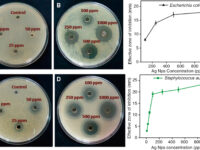
In order to test the quality of the samples produced in different parts of Histogenotech research and development unit and also to study the antimicrobial properties of some antibacterial products, the company’s microbiology unit is actively serving in this field. This unit provides the most accurate results in this field by developing a quality control plan, providing the most detailed points and requirements of the Ministry of Health. In addition, the preparation of pure and standard strains of pathogenic bacteria from reputable European companies to benefit from quality control programs and comparison with pathogenic organisms in patient samples, has enabled the collection to provide up-to-date topics for student research. Preparation and use of efficient and diverse antibiotic discs with surveys of bacteriologists and microbiologists, as well as the preparation of all commercial culture media for bacterial detection, has led to a dynamic R&D environment to provide services to production units. Histogenotech Company has been able to conduct various training workshops in this regard in the written inspection and internal audit programs, in order to use the opinions of the laboratory audit team and complete the microbial department programs.Extraction of antibiotics from fungi
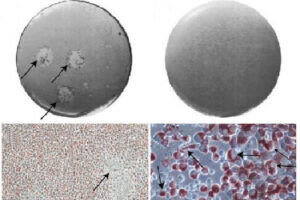
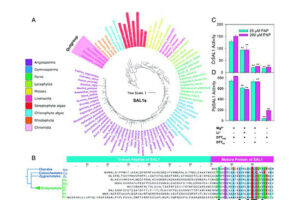
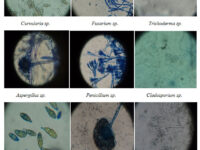
Researchers are looking to discover new antibacterial drugs and antibiotics with different primary sources, according to the World Health Organization (WHO). Fungi are one of the biological organisms that have been highly regarded by researchers at the Histogenotech Research Center due to their high diversity and high growth rate. They are known as a rich source of antibiotics and antioxidants. Therefore, research on the production of antibiotics from fungal sources is underway, and access to a new source of antibacterial could open new horizons in modern medicine. The study of fungi is very important in terms of new compounds. Inocutis levis, for example, is a yellowish-brown fungus that grows on the trunks of living trees. Recent studies have shown that this fungus prevents high blood fats and also has the property of decrease blood sugar and regulating insulin in type 2 diabetes. Since more than 100 animal models have been designed in Histogenotech, studies of infectious and diabetic skin lesions have been used to evaluate the efficacy of antibiotics derived from fungi.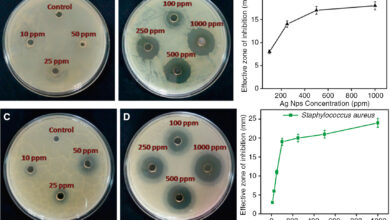
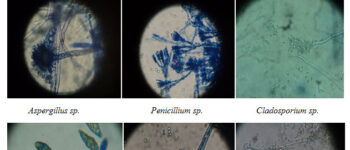
Isolation and identification of fungi for antibiotic production
One of the sources of natural products is fungi. These biological organisms, in order to protect themselves against environmental damage caused by bacteria and viruses produce different active ingredients including some natural compounds such as antibiotics such as penicillin and pleuromutilin, cholesterol-lowering drugs such as lovastatin, compactin and immunosuppressing agents like mycophenolic acid and cyclosporin. On the other hand, a wide range of fungi with a variety of carcinogens such as aflatoxins, lethal toxins such as alpha-amanitin, industrial fungicides such as strobilurin, food dyes such as azafilone, hormones such as gibberellin and psychotropic substances such as silosibine have found a special place in the process. At animal department of Histogenotech Company, various types of animal models are being developed, especially in the field of various cancers or diseases of the nervous system. In this regard, the use of fungal compounds such as alpha-amantine in the treatment of liver cancer, the use of silosibin in modeling Alzheimer’s and many other models are studied.Preparation of bacterial and viral vectors
The use of transgenic animals or transgenic plants to increase productivity and produce food products with higher volume and better quality is one of the achievements in the field of biotechnology in the present century. In this way, gene transfer and production of transgenic animals, help us to create animal models for the study of various diseases and can be used as a tool to produce a variety of drugs and recombinant compounds. Due to the key role of biotechnology techniques in the design of modern pharmaceutical products, experts in the field of Histogenotech with free consultation and design studies in the use of viral vectors, tried to create a cell bank of transgenic or transgenic cell lines to be able to science research Basic medical use it. Thus, in the previous activity of these researchers based in cellular and molecular laboratories, microbiology and biotechnology, the use of lentiviruses with different structures designed to manipulate cell lines or to track transplanted cells has been implemented so far. Viral vectors of various forms have been used to transmit genes and produce transgenic animals, including by direct injection of recombinant and gene-carrying viruses into target tissue or treatment of stem cells with recombinant virus, followed by transfer of recombinant cells to Target tissue or treatment of embryonic cells in the early embryonic stagesYou may find the answer to your question
Frequently Asked Questions by Customers
Stem cells are more resistant to changes in the structure of DNA because the body’s main reserves are in the regeneration of damaged or growing tissues. On the other hand, the membrane of cancer cells and stem cells, with some cell pumps, resist the entry of compounds into the cell. However, due to their high ability to repair, these cells are widely used in biotechnology and can be easily manipulated with new techniques and materials.
Purification of proteins or secretions from bacteria and fungi can be done in several different ways. Purification using some salts such as ammonium sulfate, the use of dialysis bags with different pore sizes based on protein molecular weight, chromatographic columns with different methods can also purify secreted proteins based on how they work including Gel-Filtration Chromatography and Ion-Exchange Chromatography, Affinity Chromatography and High-Pressure Liquid Chromatography.
There are several methods for tracking cells in vivo, based on fluorescent dyes using microscopic imaging. These tracers include BrdU (Bromodeoxyuridine), GFP (Green Fluorescent Protein), Hokhest, CM-DiI. Each of these compounds reacts with different parts of the cell and has a different lifespan and amount of color during cell divisions.
Based on the purpose of a study, gene carriers can be selected from viruses with different genomic structures. These carriers include the vectors Retrovirus, Lentivirus, Adeno virus (AV), Adeno-associated virus (AAV), and Herpes. Each of these vectors is licensed for research or clinical use, and only some of them are licensed for therapeutic use.
The production of organs from one species in the body of another species can be done under the name of chimera species. In other words, some organs of the body such as liver, cartilage, some organs such as earlobes have been successfully produced in animals for human use. Researchers hope to meet the human need for organ transplants by producing human tissues in animals.
Due to structural differences in the DNA and organs of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, the production of recombinant products from these cells is different. Thus, due to the high rate of proliferation of prokaryotic cells and the lack of some cellular components, processes such as phosphorylation, acetylation and glycosylation, called post modification, are often not performed. On the other hand, some changes or forms of protein called protein folding are generally not present in prokaryotic secretions.
Production of transgenic products such as transgenic plants has started in Iran several years ago. However, like all modern sciences, it has its critics. The most important criticisms are related to environmental, ecological issues and changes in the human genome and other species that consume these plants. One of the most important benefits of these species is having pest resistance genes, genes resistant to temperature changes and genes that are effective in accelerating the growth and development of these species, which can continue in the body, although there is no special evidence in this regard.
The use of bioinformatics has a tremendous impact on the progress of recognizing effective therapies, diagnosing some diseases, and producing a variety of pharmaceutical products. With the help of this knowledge, it is possible to estimate which receptors have role in the body communicates more strongly or which receptors are inactivates. Accordingly, the role of a drug can be estimated in the treatment process and also can be evaluated the effect of the drug on cell structure.