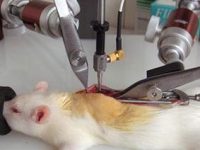
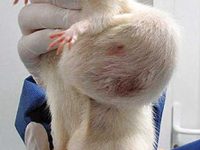
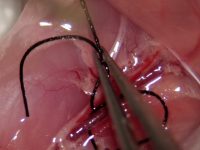
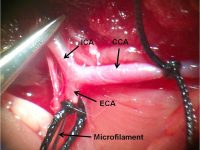
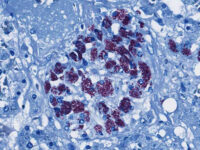
Animal study
Research on mice, rats, rabbits and other laboratory animals
Some services performed in histogenotech :
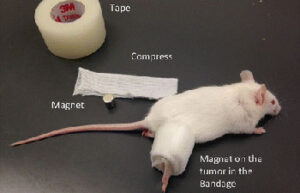
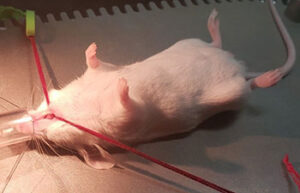
- Maintenance and replacement of mice and rat bandages
- Surgery and biopsy
- Blood sampling from the heart, tail vein, jugular vein and ocular sinus
- Animal injections: subcutaneous, intramuscular, intravenous and peritoneal
- Oral administration of the drug using gavage
- Performing animal sports techniques: treadmill, swimming, ladder
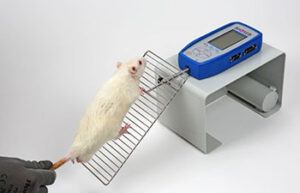
- Behavioral tests by Maurice Watermass, Shuttle Box, Openfield, Garcia, Novell Object, Elevated body
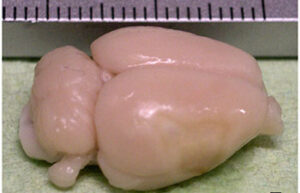
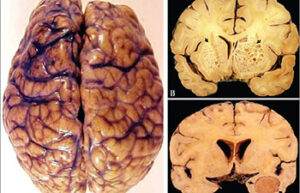
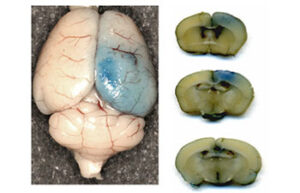
- Mice and rat brain edema test
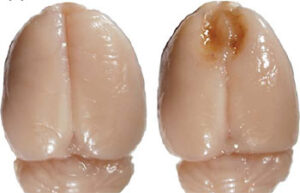
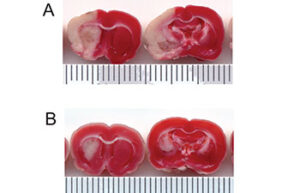
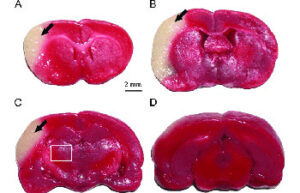
- Mice and rat brain TTC test
- Evaluation of brain Evans blue staining test in rats and mice
- Determining the reproductive cycle of mice and rats
- Create and induce a variety of animal models

Achieving any accurate animal studies requires access to the suitable facilities for working with laboratory animals, proper maintenance and breeding in a place that fully complies with the standards of laboratory animal breeding and with advanced and up-to-date equipment and facilities. In this regard, Histogenotech Research Center, with many years of experience and experienced specialists, carries out extensive activities in order to comply with the principles of standard care and practice of laboratory animals.
The many similarities between animals and humans, the short lifespan of animals and the determining of the studied factors in an appropriate period of time, as well as the possibility of controlling the experimental conditions are some of the advantages of using animals in clinical research.
Complete introduction of animal studies services
Maintaining and bandages in mice and rats
Care of laboratory animals according to the wide range of models of wounds, burns and surgeries and the specific conditions of each model is one of the most basic services of an animal laboratory. In Histogenotech Company, bandages of laboratory animals is performed to evaluate the healing process, prevent infection and prevent bleeding of wound and burn models.
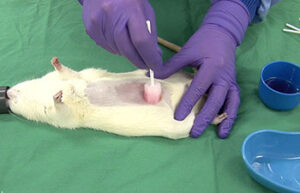
Surgery and biopsy
Laboratory animal surgery is performed to induce animal models such as ischemia, testicular occultation, immunodeficiency, and others. Also, some studies are perform to detect specific proteins or to observe the effect of variables on different tissues of the animal’s body.
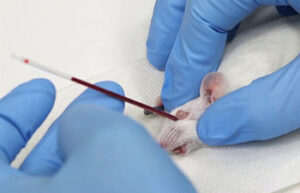
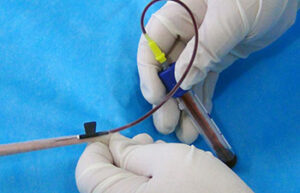
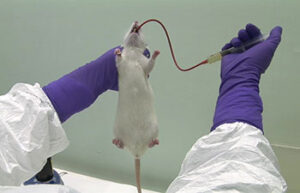
Blood sampling from the heart, tail vein, jugular vein and ocular sinus
Blood sampling from the heart, tail vein, jugular vein and ocular sinus Receiving blood from laboratory animals is essential for a wide range of in vitro and in vivo studies. Blood sampling procedures performed in the Histogenetic Animal Studies Laboratory include blood sampling from the heart, tail vein, jugular vein, and ocular sinus.
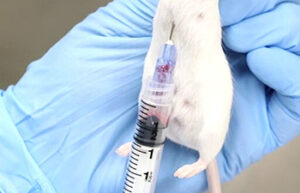
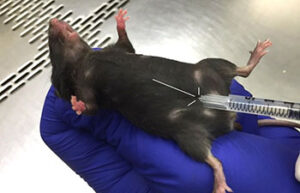
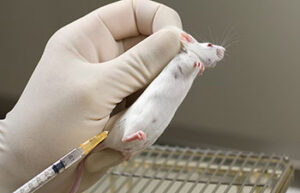
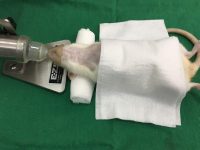
Perform animal injections
One of the most important services in the Animal Studies Laboratory is the types of injections that are performed correctly in order to deliver the drug to the living body or to create some models such as azoospermia model and cancer tumor model. In Histogenotech Company, various subcutaneous, intramuscular, intravenous and peritoneal injections are performed on mice, rats, rabbits and other laboratory animals.
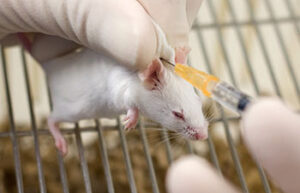
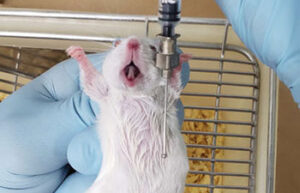
Oral administration of drugs
When a study needs to investigate the effect of a particular food or oral drug on a laboratory animal, it is used orally or by gavage, where the substance is delivered directly to the living stomach. In Histogenotech, the gavage technique is performed on rats and mice for therapeutic studies of various drugs.



Animal sports techniques
Exercise is considered as an important intervention for the treatment and prevention of many diseases such as osteoarthritis, obesity, hypertension, Alzheimer’s and others. In Histogenotech, various aerobic, endurance, resistance, periodic and exercise techniques are performed through treadmills, swimming, and ladders to study the effect of exercise on various animal models such as diabetes, fatty liver, Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and cardiac ischemia.
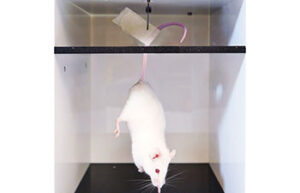
Behavioral testing
Behavioral tests are used to assess sensory-motor function, learning, memory, and psychological factors (stress, anxiety, and depression) in animals. These tests can measure the animal’s ability to solve a daily task. In addition, they are very suitable and effective in evaluating the effect of drug and exercise interventions on animal models.
Mice and rat brain edema test
Cerebral edema is caused by severe traumatic brain injury. In Histogenotech, various injuries to the brain caused by damage to the blood-brain barrier, cerebral ischemia, trauma, etc. are used to evaluate the therapeutic side effects of a drug called cerebral edema test.
Mice and rat brain TTC test
The TTC test is used to distinguish metabolically active and inactive tissues. In pre-clinical treatment studies of stroke, TTC staining is commonly used to show a reduction in postoperative infarct volume. The TTC stains the active cells bright red and the damaged cells do not stain.
Evaluation of brain Evans blue test in rats and mice
Disruption of the blood-brain barrier after cerebral ischemia leads to the outflow of plasma components into the brain parenchyma, the severity of this disruption is directly related to the size of the lesion. Evaluation of blood-brain barrier disorders is performed using Evans Blue staining, which has a great importance in neurological research.
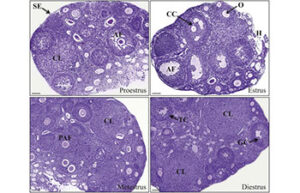
Determining the reproductive cycle of mice and rats
Determining the sexual cycle is very important for assessing the functioning of the reproductive system in animal studies. In the Histogenotech animal laboratory, the identification of the reproductive cycle is used to evaluate the types of interventions made in the reproductive cycle in vaginal secretions.
Create a variety of animal models
Create diabetic model
diabetic model
Diabetes is a complex disease that affects about 4% of the world's adult population. This disease is a chronic metabolic disorder that results from a defect in insulin secretion. In the Histogenotech, induction of diabetes model using streptozotocin (STZ) is induced in three types of severe diabetes model, similar to human type 1 diabetes model and mild diabetes model, as well as type 2 diabetes model using STZ and high-fat diet.
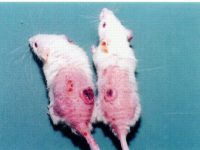
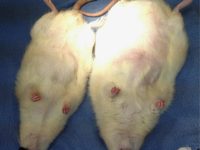
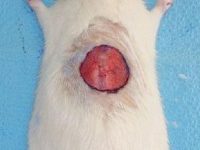
Create burn and wound patterns
Create burn and wound patterns
Induction of burn and wound models is performed to study the healing process and study the effects of new types of wound bandages, drugs and plant extracts on healing and reducing healing time. In the animal studies laboratory of Histogenotech, wound and burn models are created in different sizes and dimensions and different depths (different layers of skin) and varying degrees.
Spinal cord injury model
Spinal cord injury
Spinal cord injury is known as one of the most valuable models in better understanding the physio-pathological mechanisms of this disease and evaluating new treatment methods. In the Histogenotech, Spinal cord injury model induction is performed due to spinal cord injury through bruising, compression, spinal dislocation, incision, and amputation of spinal cord tissue. BBB motor behavior test is used to confirm spinal cord injury with different intensities.
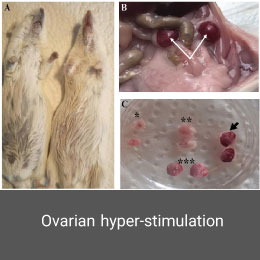
Ovarian hyper-stimulation model
Ovarian hyper-stimulation is a life-threating syndrome that can occur during infertility treatment using ovulation induction and controlled hyper-stimulation methods. This model is induced in the Histogenotech laboratory with PMSG and HCG hormones.Varicocele model
Varicocele is one of the most common treatable causes of infertility in men, occurring in 15 to 20% of men. One of the most important obstacles in the study of varicocele is that it is almost found in humans, which is why the development of animal models of varicocele is of particular importance in infertility studies. Histogenotech developed this model by performing microscopic surgery on laboratory animals.Azoospermia model
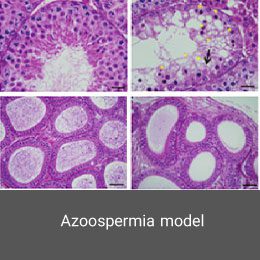
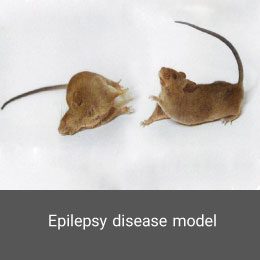
Azoospermia is one of the most common types of infertility in men, in which there is no sperm in the ejaculate. Among its causes are obstruction of the genital tract, hormonal problems. In the Histogenotech, azoospermia is induced by intraperitoneal injection of Busulfan drug at a specific dose and time period. Confirmation of this model is determined by spermo-gram test.Epilepsy disease model
Epilepsy is a multifactorial neurological disorder caused by an increase in abnormal nerve secretions or excessive irritability of neurons in the body, leading to seizures or abnormal shaking in the body. In the animal studies unit of Histogenotech, epilepsy is induced by systemic and cerebral administration of Kainic acid through brain surgery by a stereotaxic device. Electroencephalography (EEG) is used to confirm the induction of this model.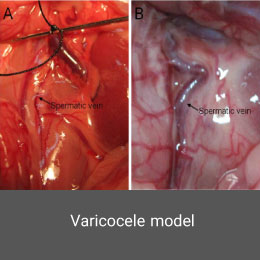
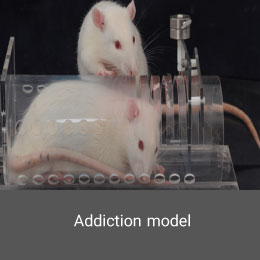
Addiction model
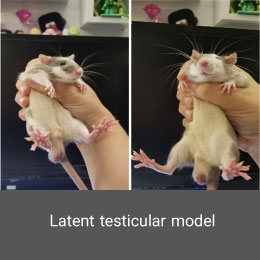
Creating drug addiction model is performed in the Histogenotech Co. with the permission of relevant organizations and institutions. Depending on the type of study, these substances can be administered orally or by injection to laboratory animals such as mice and rats.Latent testicular model (cryptorchidism)
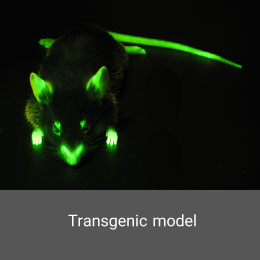
Although cryptorchidism is the most common congenital anomaly in boys, human knowledge about the causes of cryptorchidism is still limited. Animal models are used to better understand the pathophysiology and treatment of cryptorchidism. In the Histogenotech Co., a latent testicular model is induced using surgery.Transgenic model
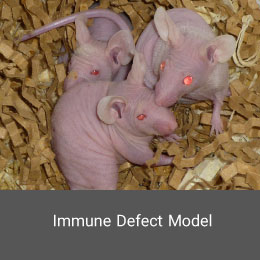
Transgenic animals have become key tools in genomic studies and the development of human disease models for the study of new drugs. Transgenic models involve adding external genetic information to the animal genome or inhibiting the expression of a specific gene in the animal’s body.Immune Defect Model
In this model, the immune system is weakened and become susceptible to infections, tumors or similar diseases. Animal models of immunodeficiency can be created using physical, chemical, surgical, or genetic manipulation methods. This model is also induced using gamma ray in the Histogenotech Co.Alzheimer's disease model
Alzheimer's disease
Due to the lack of treatment for Alzheimer's disease, conducting studies in this field become highlighted. Histogenotech Co. create Alzheimer's model using both amyloid beta and STZ (Streptozotocin) based on more than a decade of experience in Alzheimer induction. Behavioral and conformational tests for Alzheimer's disease is Maurice Watermass, Shuttle Box and Openfield tests.
Fatty liver model
Fatty liver
Nowadays, one of the most important public health problems in the world is overweight and obesity. Therefore, in the animal study unit of Histogenotech, studies on the occurrence of obesity and its prevention and treatment are a priority of research. Histogenotech induces the fatty liver model by prescribing high-fat diets to rats and mice.
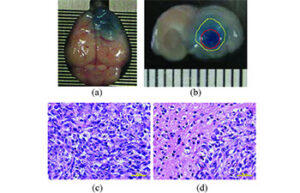
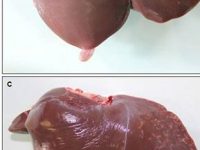
Cancer tumor model
Cancer tumor
Cancer is the second most common cause of death in the world after cardiovascular disease. Laboratory animal models are an important and powerful tool in advancing cancer research. Histogenotech offers a variety of cancer models with the efficiency of a rich bank from different types of cancer cell lines and relying on its expert researchers.
Stress model
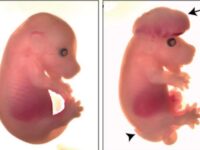
Stress is a mental condition that affects a person’s daily functioning and imposes a high cost on public health. Charles Darwin’s early findings showed that animals and humans have similar characteristics in the expression of emotions, which can be considered the starting point for the use of animal models in this type of study. In Histogenotech, the stress model is created using a variety of exposures to sound, vibration, and so on.Embryonic Defect Model
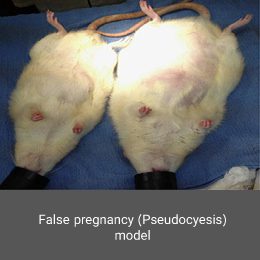
Congenital malformations are one of the major global health problems worldwide. Investigation of the causes, treatment and prevention is one of the most important research chapters of the Histogenotech unit of embryological studies. Animal models of embryonic defects are induced in mice and rats using a variety of mutagenic drugs.False pregnancy (Pseudocyesis) model
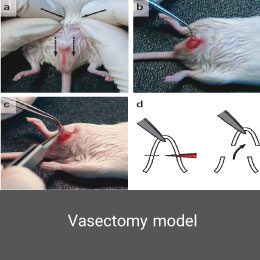
A condition in which a non-pregnant woman believes she is pregnant and shows many signs and symptoms of pregnancy. This disorder affects both the psychological and endocrine dimensions. Animal models are a very effective tool for better understanding the mechanisms of this disorder. In the Histogenotech, false pregnancy models induced using estrogen hormone and male azoospermia model.Vasectomy model
Vasectomy is a form of contraception in men that reduces sperm count to zero during ejaculation. Vasectomy is a subset of the azoospermic model induced by microscopic surgery in mice or rats which is perform at the Histogenotech research center.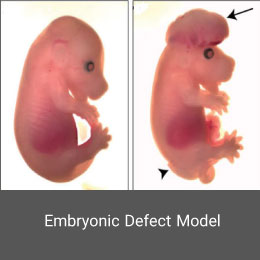

Polycystic ovary syndrome model
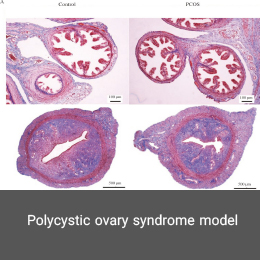
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal disorder characterized by elevated androgen levels, menstrual irregularities, or small cysts in one or both ovaries. The causative agent of this disorder can be morphological (polycystic ovary) or mainly biochemical (hyperandrogenic). In the Histogenotech, the PCOS model is induced using estradiol valerate over a specified time period and dose.Organ transplant model
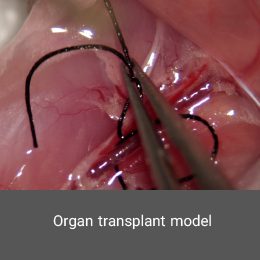
Organ transplantation has become a successful and acceptable treatment for organ failure in the final stage of treatment. Histogenotech offers a variety of tissue transplant and organ transplant models for researchers with the benefit of experienced specialists and equipped animal and cell laboratories.Hypoxia model
Hypoxia is a condition that is not enough to maintain cell homeostasis due to a lack of oxygen in the blood and eventually enough tissue at the surface. This condition usually occurs for climbers at high altitudes due to lack of oxygen in the air. In the Histogenotech, this model is available in different percentages of ambient oxygen deficiency.Viral infection model
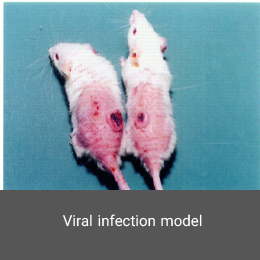
Animal models of viral infection make it possible to identify immune factors that protect the host against viral infection or enhance the immune response. In addition, such animal models make it possible to develop new vaccines. In the Histogenotech, the infected models with a variety of respiratory viruses are available.MS model
MS
MS is a progressive and degenerative disease of the myelin sheath in the nerve fibers located in the central nervous system. Histogenotech, using the expertise of its neuroscientists, uses cuprizone and EAE to induce this model. In order to evaluate the creation of this model, Open field and Narrow Beam and Horizontal ladder behavioral tests are used.
Ischemic model
Ischemic
Ischemia or stroke is a condition in which the blood flow to the tissue is restricted and leads to a lack of oxygen needed for cellular metabolism. Ischemia is usually caused by a problem with the blood vessels and causes tissue damage or dysfunction. In the Histogenotech, ischemia of the heart is induced by Isoprenaline or by surgery and coronary artery occlusion, while cerebral ischemia is induced unilaterally or bilaterally by surgery and occlusion of the common carotid arteries.
Parkinson's model
Parkinson
Parkinson's disease is a progressive neuropathological disorder that mainly affects dopamine-producing neurons in the brain. Histogenotech induces Parkinson's disease model using 6-hydroxy dopamine (6-OHDA) by experienced specialists and up-to-date equipment, and confirm this model with rod behavioral tests, rotation tests, open fields, shuttle boxes, and uses Elevated body swing test.
شاید جواب سوال خود را بیابید
سوال های متداول مشتریان
بله. برای نگهداری از عامل میکروبی کافیست از یک محیط کشت غنی مایع همچون تریپتی کیس براث و یا مایع عصاره قلب و مغز استفاده شود. پس قرار دادن تعداد لازم از باکتری، از گلیسرول برای جلوگیری از تخریب باکتری ها به واسطه سرما استفاده می شود. اگر عامل میکروبی را برای چند ماه بخواهیم نگهداری کنیم از دمای منفی 20 درجه سانتیگراد، و برای نگهداری سالیانه از دمای 80- استفاده می شود.
انتقال نمونه میکروبی ایزوله شده و تخلیص شده به آزمایشگاه غالبا به دوصورت تازه (Fresh) و لیوفیلیزه انجام می پذیرد. در صورتی که نمونه به صورت لیوفیلیزه برای انتقال آماده شود اغلب در آمپول های خلا و در دمای اتاق منتقل می شود. در حالی که نمونه تازه بر روی محیط کشت جامد و یا مایع منتقل می گردد، دمای یخچال (ایجاد دمای یخچال توسط پک یخ قابل تامین است) برای آن باید استفاده گردد. ذکر این نکته مهم است که ظرف انتقال عامل میکروبی باید حاوی اطلاعات کامل باشد و همچنین فاقد هرگونه نشتی باشد و در شرایط ایمنی زیستی استاندارد منتقل گردد.
مهم ترین دلایل برای اینکه محیط جامد به خوبی بسته نشده است شامل این موارد است: میزان آب مقطر اضافه شده بیشتر از دستورالعمل است، میزان پودر وزن شده کمتر از میزان مشخص شده در دستورالعمل می باشد، میزان pH محیط به درستی در محدوده خنثی قرار داده نشده است، تاریخ مصرف محیط کشت گذشته و محیط قابل استفاده نمی باشد.
در مطالعات میکروبی برای استفاده از باکتری ها لازم است در هر مرحله بدانیم بر روی چه تعدادی از میکروب در حال انجام کار هستیم. به این منظور برای استاندارد سازی غلظت ها از نیم مک فارلند استفاده می شود که اگر در طول موج 510 اسکپتروفتومتر خوانده شود، حاوی 108* 1.5 باکتری خواهد بود. امروزه نیم مک فارلند به صورت تجاری قابل تهیه است و بهتر است برای جلوگیری از کم شدن کدورت آن، در تاریکی نگهداری شود. کارایی این محلول در تست های بررسی حساسیت میکروبی، تهیه کدورتی مشابه با نیم فارلند توسط باکتری مورد مطالعه برای انجام تست می باشد.
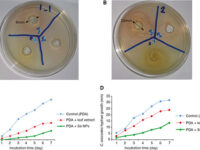
برای بررسی میزان هاله ی ایجاد شده کافیست از خط کش مدرج استفاده شود تا قطر هاله ایجاد شده اندازه گیری و با واحد میلی متر یادداشت شود. برای بررسی و آنالیز نتایج از دستورالعمل CLSI استفاده که هاله اندازه گیری شده با استاندارد جهانی مقایسه شده و میزان حساسیت و مقاومت به شکل مقاوم – مقاومت میانه – حساس گزارش می گردد.
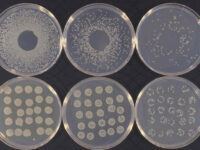
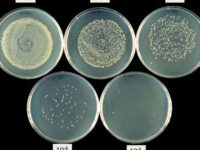
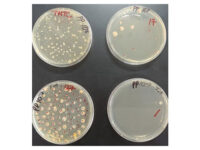
برای شمارش تعداد کلنی میزان 10 پلیت میکروبی که رقت های متفاوتی از نمونه در آن پخش شده شمارش می شود. میزان قابل شمارش کنی ها اغلب بین 30 – 300 کلنی می باشد و در انتها نتایج شمارش کلنی باید به شکل CFU/gram و یا CFU/mL گزارش شود ( بسته به نوع نمونه که مایع است یا جامد). واحد CFU واحد استاندارد شمارش کلنی است که برای هر باکتری گزارش می شود.
برای بدست آوردن کمترین غلظت از آنتی بیوتیک که توان از بین بردن باکتری مورد نظر را دارد، کافیست یک نمونه از آخرین لوله بدون کدورت در تست ماکرو براث دایلوشن را همراه با دو لوله با غلظت بالاتر را جداگانه در یک محیط کشت جامد، کشت دهیم. پس از 24 ساعت، رشد آن در محیط جامد را بررسی می کنیم. غلظتی که رشد نکرده است به عنوان حداقل غلظت کشندگی گزارش می گردد.
بله، تست های متفاوتی وجود دارد که توان اندازه گیری خواص ضد میکروبی فرآورده های گیاهی را بدست آورد. رایج ترین و کم هزینه ترین آن انجام تست دیسک دیفیوژن است. با آنکه تا به امروز دستورالعمل استانداردی برای آن وجود ندارد ولی میتوان میزان عدم رشد را در محیط جامد مشاهده نمود.
You may find the answer to your question
Frequently Asked Questions
Depending on the type of animal, the physical and chemical properties of the drug, one of the enteral and parenteral methods is used to enter the drug or substance into the body. In the entral method, the drug enters the gastrointestinal tract directly and is absorbed through the stomach and intestinal wall. Other cases in which the substance does not enter the body through the gastrointestinal tract (injection) or topical (topical) include pre-antral methods. The dose and gavage and injection time are determined based on the type of study, previous studies and the animal’s body weight. Injections include Intra-cardiac, Intra-peritoneal, Intra-dermal, Intra- muscular, Sub-cutaneous, and Intra-venous.
Blood samples are usually taken from mice, rats and rabbits. In rats, the blood volume is 50 ml / kg, and at each blood sampling, 10% of the total volume can be taken. However, in mice, due to the small volume of blood, collecting blood samples is difficult and finally 1-2 ml can be collected from heart. Blood sampling methods in rats and mice include venous network behind the eyeball, cardiosynthesis, nail amputation and tail end, and collection of blood from veins.
After the tissue isolates from the body, lack of nutrients and oxygen causes the death of tissue cells. Bacteria and some enzymes cause disruption and tissue loss. Therefore, immediately after isolating the tissue from the body, we put it in a solution of 10% formalin (solution of 3.7% formaldehyde). Formalin binds tissue proteins together and preserves their structures. Tissue volume changes slightly after stabilization in formalin, while other fixatives such as ethanol reduce tissue volume, which is important in quantitative research. To perform some techniques, such as Western blotting, molecular technique (PCR), and ELISA, the tissue isolated from the living organism must be kept at freezing temperature (-80 °C) to prevent the destruction of proteins and other important factors.
There are four common methods for modeling cancer in mice: the chemical model, the cell line-derived xenograft (CDX) model, the patient-derived xenograft (PDX) model, and the genetically engineered mouse model (GEMM: genetically engineered mouse model). Pure or inbred strain (BALB / c and C57) is used to induce tumor by cell transplantation (CDX). Depending on the tumor, there are different cell lines for induction. In creating human tumor models in mice, the mouse’s immune system needs to be eliminated or weakened. Accordingly, in some cancer models, tumor cells are created by intraperitoneal or subcutaneous injection, which is called the heterotopic method, while in some tumor models Tumor cells are injected into a site similar to a cancer cell line, which is called orthotopic. In some tumor models, due to the fact that cell line growth is related to factors such as body hormones, it is necessary to expose the animal’s body to factors such as hormones at the same time as the cell is injected. On the other hand, according to the cell invasion and proliferation cycle (cell doubling time), the number of injected cells varies based on the characteristics of the cell line. In this regard, tumors with high proliferative capacity of 250,000 cells in a volume of 100 microliters in mice between 20 to 25 grams are injected. While in slow cell lines this amount reaches 2 to 4 million cells per 100 microliters injected into the animal.
In order to design a training model, two factors, VO2max and One-RM, are commonly used. Designing a training program and training science without considering One-RM, every move is meaningless and completely unscientific. One-repetition maximum (1RM) is the maximum weight that a muscle or muscle group can move, which is called a maximum repetition (1RM) for that muscle or muscle group. On the other hand, the VO2max factor is an important factor in the endurance status of the body during the design of a study. Maximum oxygen consumption or VO2max is the maximum amount of oxygen that the human body is able to receive in one minute. This factor is calculated in units of total body weight and per kilogram of body weight. This factor is closely related to the endurance status of the human body and aerobic activity. This test is designed to measure the amount of oxygen consumed by the heart, the amount of oxygen leaving the lungs and the aerobic capacity in exercise, which is calculated in terms of the maximum volume of oxygen entering the body per unit time (milliliters per kilogram per minute).
The procedure conditions and keeping of laboratory animals require the observance of the principles of extensive and, of course, very important laws, which must comply with the standards of the World Health Organization (WHO). However, if we are only talking about the habitat of this type of laboratory animal for research studies, it should be noted that during the study period, the characteristics of the animal habitat are stable. Changes in light, temperature, airflow and other environmental parameters can have significant effects on the results of the research project. Usually, the sleep and wake time of mice and rats is 12 hours in the dark and 12 hours in the light at a temperature of 23 °C and a humidity of 50. The movement, packaging and storage of food must be free from contamination and corruption. Shelving should be done without stressing the animal.
In the method of sacrificing an animal, the use of carbon dioxide is one of the most fundamental ways of killing. Inhalation of high concentrations of 7.5% carbon dioxide has a rapid anesthetic effect. Exposure of mice to concentrations above 80% of the gas causes anesthesia in 33 seconds. The animal is placed in the chamber, the appropriate amount of gas flow should be able to replace 20% of the volume of the chamber per minute. Rapid induction of anesthesia occurs when the animal is exposed to a concentration of 70% CO2. Gas flow should be maintained for at least one minute after the apparent clinical death of the animal. The use of injectable drugs is the fastest and safest way to sacrifice an animal. Intravenous, intraperitoneal and intracardiac injections are acceptable. Overdose of barbiturates is a common procedure. Sometimes it requires sedation or anesthesia. Intravenous or intracardiac injection of potassium chloride saturated solution can only be injected into an anesthetized animal. Other methods include cervical dislocation, guillotine amputation./p>
Studies in the field of neuroscience lead to a better understanding of brain function and the nervous system and nervous diseases. Nowadays, due to the importance of neuroscience, many projects and researches are conducted in the field of neuroscience. The majority of neuroscience studies focus on diseases such as spinal cord injury, Alzheimer’s, stroke, MS, epilepsy, Parkinson’s, and physiological sleep disorders. Behavioral tests such as the Maurice Water, Open Field, Shuttle Box, Bar Balance Test, Beam Walking Test are performed to confirm and evaluate these disease models.
For anesthesia, two different types of materials are generally used usually in combination. The first substance before anesthesia is sedatives which are prescribed to facilitate the induction and reversal of anesthesia. Diazepam, midazolam and zvalzepam have sedative, muscle relaxant and anticonvulsant effects. Also, Xylazine is the most widely used as alpha-2 agonist. The effects of this drug begin within 3 to 5 minutes after intravenous injection and within 10 to 15 minutes after intramuscular or subcutaneous administration. Which is used in the amount of 5 to 10 mg / kg of animal body weight. In the second substance is drugs which are used for anesthesia that increase the muscle tone, increase blood pressure, and have mild analgesic effects. Ketamine is a well-known member of this group and the most widely used veterinary anesthetic. Anesthesia required for surgery in rodents and rabbits can be created by combining ketamine with xylazine. In rabbits, a combination of ketamine and diazepam can be used. Ketamine absorption is followed by rapid intravenous, intramuscular, subcutaneous and intraperitoneal administration. In ketamine anesthesia, the eyelid and eye reflexes and the swallowing and laryngeal reflexes are active. Consumption of this substance is 20 to 60 mg / kg body weight. Other methods of anesthesia are inhaled, with the use of isoflurane which is more common than others, and the use of a chamber that receives the animal anesthetic gases and oxygen at the same time that is the best method used in laboratories.
The use of laboratory animals in research is used when there is no other alternative way to do so. For some aspects of medical research, there is no proper way to show the interaction of vital organs in the body during a research process. Animal research has helped to develop many important medical advances, including the development of new drugs, vaccines, the treatment of incurable diseases such as Alzheimer’s and metabolic diseases such as diabetes and hypertension, and a variety of cancers. Research on animal models in preclinical studies in various fields of medicine, especially in the prevention of respiratory infectious diseases are highly interested.