Application of turmeric in nanobiotechnology
Application of turmeric in nanobiotechnology
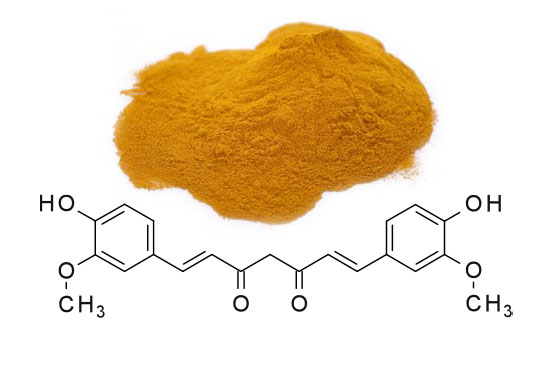
Curcumin is the most important component of turmeric It is antibacterial and a natural plant polyphenol that is extracted from turmeric root
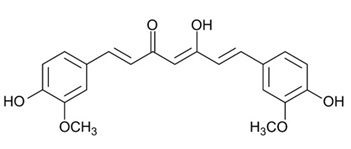
it is usually powdered with bisdemethoxycurcumin and dimethoxycurcumin. The compound is difficult to dissolve in water, with a reported solubility of about 11 ng / ml in a simple aqueous buffer at pH 5.
Curcumin is stable in acidic environment (pH 3.5-6) but unstable in neutral or alkaline conditions due to rapid hydrolysis. By eating turmeric, due to the low solubility of curcumin in salivary fluid and its poor stability in gastric and intestinal fluids, curcumin is absorbed by cells slightly. In addition, curcumin is rapidly metabolized and deformed after uptake, resulting in low bioavailability.
Research has shown that after intraperitoneal or intravenous administration of curcumin, large amounts of it are excreted in the bile in the form of tetrahydrocurcumin glucuronide (THCG) and hexahydrocurcumin (HHC). However, over the past few decades, many studies have shown that curcumin can be effective in treating liver, rheumatism, bile disorders and inflammation. In recent years, extensive research has been conducted on the anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer and anti-angiogenic properties of this Plant material.
Studies have also shown that curcumin can inhibit a variety of cancers, including blood, brain, breast, gastrointestinal tract, head and neck, liver, pancreas, colon, prostate, ovary, and skin. curcumin is also an effective anti-mutagenic agent and has been introduced by the National Cancer Institute as the third generation of prophylactic drugs in chemotherapy.
For this purpose, various nanotechnology-based drug delivery methods have been used to increase oral bioavailability, bioactivity, or the ability of curcumin to target tissue. It is predicted that with the use of nanotechnology, bioavailability will increase significantly due to the reduction of particle size and consequently the increase of dissolution rate. Therefore, nanotechnology may be the best practical way to solve the problem of dissolution and bioavailability of insoluble drugs.

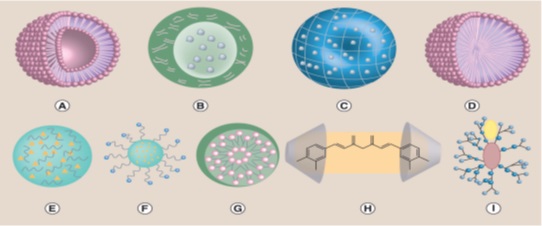
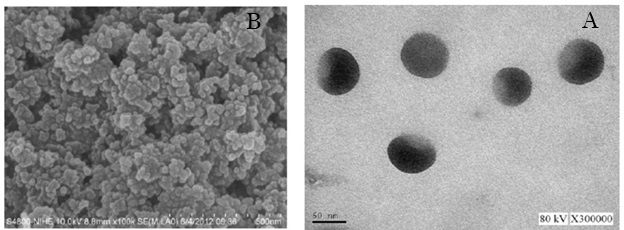
Reference:
Industrial Microbiology Laboratory – Jihad of Kharazmi University , Authors: Ensieh Salehghamari, Marzieh Azizi, Abolfazl Abbasi
Related content: Production of nanoparticles carrying plant extracts
Related services: Production of nanoparticles and nanostructures for research and treatment purposes