drug-carrier nanoparticles
drug-carrier nanoparticles
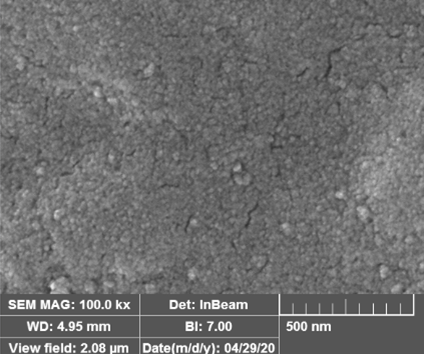
Nanoparticles are solid colloidal particles with a size of 1 to 100 nanometers. In recent years, nanoparticles have been able to attract the attention of many researchers and scientists in the Drug Delivery System (DDS). The use of nanoparticles as a drug carrier has made new advances in medicine and pharmaceuticals by improving drug performance and reducing its side effects. Various materials such as natural and synthesized polymers, metal particles, lipids, etc. are used to produce nanoparticles, which can have different shapes (morphologies) and sizes depending on the method of production and synthesis. The use of nano carrier-based drugs is widely accepted around the world and has a significant place in global markets. Histogenotech Company, relying on its internal knowledge and its research and R&D unit, has been able to take an important step in the production of various nanoparticles as drug carriers. With a well-equipped and advanced laboratory unit, Histogenotech has been able to carry out numerous researches in various scientific research projects such as sport physiology, cancer, stroke, Parkinson’s, and Alzheimer’s.
Production of nanoparticles carrying Bevacizumab
Uses of Bevacizumab
– Treatment of colorectal metastatic cancer
– Treatment of lung cancer
– Treatment of progressive glioblastoma
– Treatment of metastatic kidney cell cancer
In Histogenotech Co. , by employing a multidisciplinary approach including chemical engineering, pharmacy, polymer engineering, and chemistry, Boasizumab is encapsulated. The main aim of this study (production) is to conduct research in various fields including cancer treatment in animal models.
Due to the toxicity of synthetic polymers, natural polymers such as chitosan, alginate, gelatin, collagen, etc. are used to encapsulate Bevacizumab. For this purpose, the technique of gel production by the ionization method has been employed. The nanoparticles are finally isolated using centrifuges and washed several times using deionized water to remove biopolymers and additional chemicals. Then, for ease of use, we add a certain amount of deionized water to the nanoparticle pellets and start sonication to reach a uniform mixture. The final colloids are stored in 5 ml vials at 4°C.
Related Scientific Content: Production of nanoparticles and nanomaterials –