Embryology research services with modern methods such as IVF
Embryology services provided by Histogenotech
- Isolation and washing of sperm
- Manual spermogram and CASA
- Specialized staining of sperm chromatin
- Provide wash culture medium and sperm concentration gradient
- Sperm, egg and embryo manipulation medium
- Stimulation of ovulation and separation of ovarian follicles
- Egg preparation and in vitro fertilization (IVF)
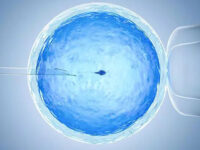
- Intracytoplasmic injection (ICSI)
- Evaluation of apoptosis in sperm, eggs and embryos
- Evaluation of oxidative stress in ovaries, testes, sperm, eggs and embryos
- Investigation of the concentration of antioxidants in tissues and cells
- Fetal transfer to the uterus in a false pregnancy model (Pseudocyesis)
- Frozen embryos, sperm and eggs
- Provides freezing and thawing of embryos and eggs
- Training in intracytoplasmic injection technique (ICSI) at the clinical level

Embryology study services
Isolation and washing of sperm
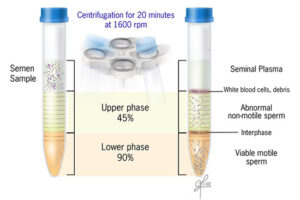
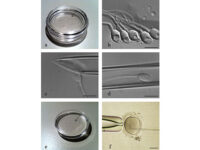
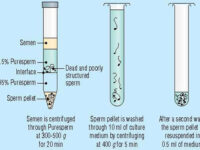
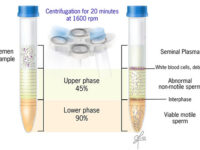
Ideal sperm isolation should be rapid, easy, and cost-effective, to separate motile sperm, not to damage sperm or abnormal changes in isolated sperm cells, remove inactive sperms and other cells including leukocytes, bacteria, toxins or bioactive substances such as decapitation factors or reactive oxygen species (ROS). In the conventional swim-up method, functional sperm can be centrifuged in close cell-to-cell contact with defective sperm or leukocytes. As a result, they cause massive oxidative damage to the plasma membrane of sperm by ROS and consequently sperm function. Thus, other separation methods such as concentration gradient or sperm filtration with Sephadex column and membranes are suggested. These methods are widely used in Histogenotech with the beneficial of experienced specialists.
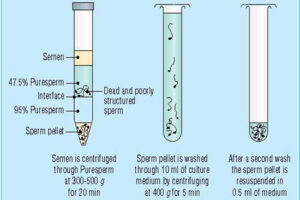
Provide wash culture medium and sperm concentration gradient
Sperm washing is often performed to obtain high-quality specimens (greater sperm count and motility). Different methods of sperm separation can be classified into migration methods, density gradient centrifuges and filtration methods. A prerequisite for all methods of sperm migration and motility. For density gradient centrifuges, isolated culture media such as Ficoll and Percoll have been introduced. Glass wool filtration and sperm filtration with Sephadex columns and membranes are alternative separation techniques. The typical medium available in andrology or embryology laboratories as well as the embryology department of the Histogenotech, Ham F-10 and HTF is enriched with HAS (Human Serum Albumin). These methods are used frequently in the master and PhD thesis of different branches of developmental biology, embryology and dissection sciences,.
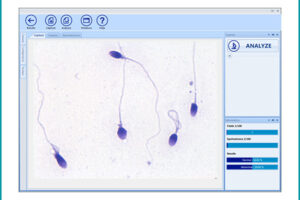
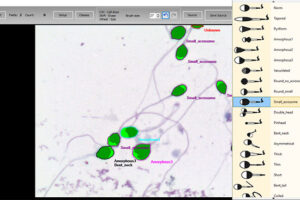
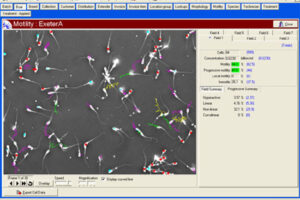
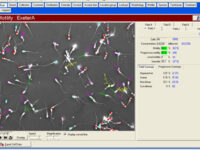
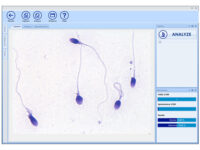
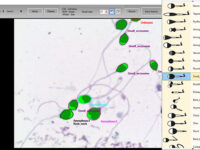
Manual spermogram and CASA
Spermogram is a laboratory analysis of male sperm that is performed to estimate the fertility of sperm. In an effort to make semen quality assessment more targeted and accurate, tools for computer-aided semen analysis (CASA) have been developed. Using CASA, several specific motility parameters can be obtained that describe sperm motions (Progressive, Motile, Sluggish, Immotile) in more detail. Since sperm concentration is a strong predictor of fertility in men, the Histogenotech Reproductive Research Laboratory has developed various research projects on the use of supplements (vitamin C, L-carnitine, pentoxifylline, various herbs) to increase the rate of fertility. The motility and ultimately fertility of adult male mice is maintained in normal sperm culture medium or frozen and thawed sperm.
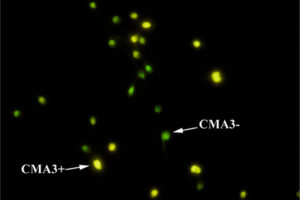
Specialized staining of sperm chromatin
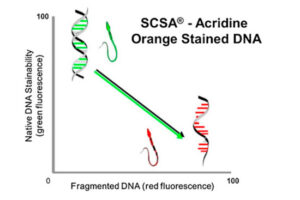
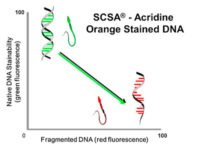
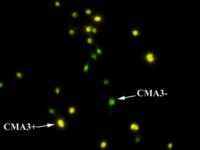
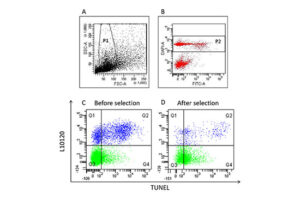
The diagnosis of male infertility is mainly based on the concentration, motility and morphology of semen parameters based on the World Health Organization (WHO). However, none of these parameters can predict a couple’s fertility potential. Sperm Chromatin Structure Test (SCSA) is a flow cytometric test that measures the sensitivity of sperm DNA to the denaturation of in situ acid-induced DNA. DNA fragmentation of sperm, measured by SCSA, is a predictor of successful pregnancy and can be used as a tool for screening, counseling, and treating infertility without cause. Tunnel method for sperm DNA degradation, chromatin staining with chromomycin A3 staining, acridine orange staining, Comet Assay method, measuring DNA degradation by halosperm method are all methods that can be performed in Histogenotech.
Sperm, egg and embryo manipulation medium
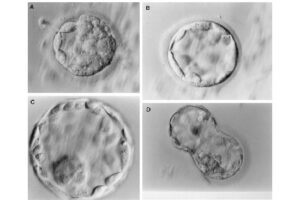
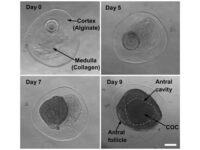
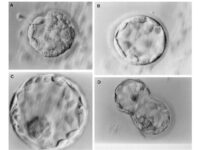
Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI), in vitro fertilization (IVF), in vitro egg maturation (IVM) and in vitro sperm preparation require different culture media called sperm, egg and embryo manipulation medium. In order to achieve a successful fertility, sperm must maintain their motility and survival in a suitable culture medium in terms of pH, osmolality and sufficient nutrients, and reach the egg to be fertilized. On the other hand, MI or MII oocytes in primary (primary), secondary (preantral), tertiary (graph or antral) follicles must maintain their adult maturity or survival in the laboratory in order to fertilize with quality sperm, quality embryo Create a 2PN in step. In order to increase the fertility rate, a suitable embryo culture medium will enable 2PN embryos to grow into 2 cells, 4 cells, 8 cells, 16 cells, or morula and blastocysts.
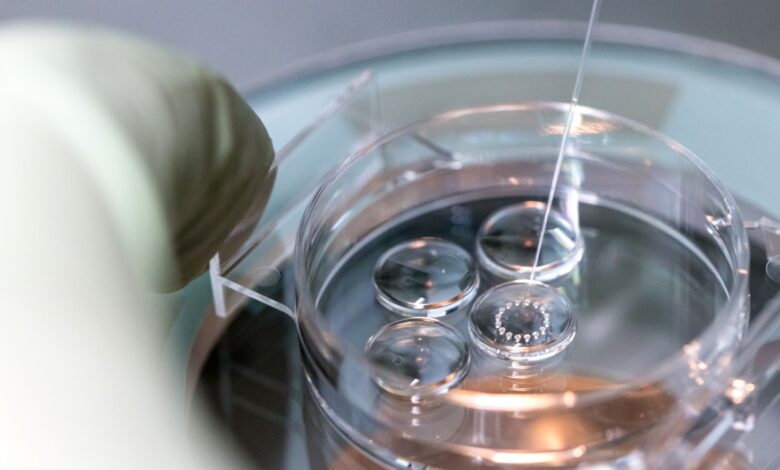
Egg preparation and in vitro fertilization (IVF)
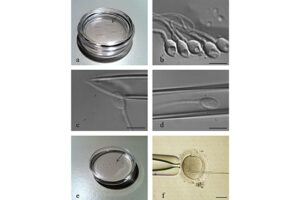
In vitro fertilization is an assisted reproductive technique (ART) commonly referred to as IVF. In vitro fertilization involves the fertilization process, in which an egg cell and a sperm cell combine manually in the laboratory. The resulting blastocyst or morula embryos are transferred into the uterus to continue the developmental process and implant in the body to continue the developmental stages. Other methods of assisted reproduction include the transfer of male germ cells into the fallopian tube (GIFT) and the transfer of embryos at different stages of development into the fallopian tube (ZIFT). In order to perform microinjection processes (ICSI) or in vitro fertilization (IVF) and egg freezing, egg preparation (incubation) is required. Thus, the eggs collected during ovulation or puncture are collected at different stages of nuclear maturation, including GV, GVBD, and MI eggs in a Histogenotech laboratory, and after being placed in a fertilization drop, become a fertilized MII egg or a 2PN embryo.
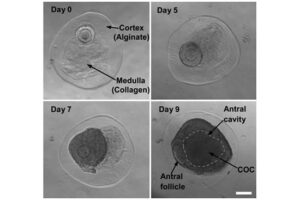
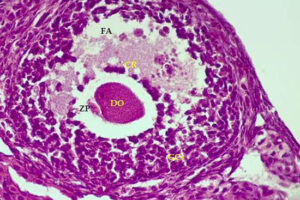
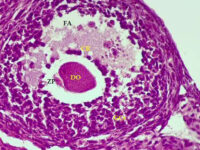
Stimulation of ovulation and separation of ovarian follicles
Oocyte pick-up (OPU) or in vitro fertilization (IVM) or in vitro fertilization (IVF) is one of the most common aspects of assisted reproductive technology. Because in vitro fertilization requires the injection of ovulation-stimulating hormones for in vitro fertilization, access to mature eggs, with a limited number and not more than usual, can lead to a successful fertilization. In order to receive more eggs and achieve more embryos for a successful in vitro fertilization, it is necessary to create hormonal conditions appropriate to the sexual cycles of female mice. In this regard, by injecting gonadotropins such as HMG, Letrozole FSH and PMSG, more primitive or primary follicles can be stimulated in the human or mouse body to resume the process of ogenesis and mature. The collected eggs are located inside the follicles with different dimensions and stages of nucleus maturation. After harvesting in the Histogenotech embryology laboratory, they are germinated (removal of cumulus cells around the egg and granulosa cells) and after culture in a suitable medium using oocyte culture, washed sperm are fertilized.
Frozen embryos, sperm and eggs
Freezing or embryo cryopreservation to keep the fetus in liquid nitrogen for a long time at different developmental stages from 2 nuclei to blastocysts is common in assisted reproduction laboratories. Egg freezing requires nutrient culture medium with osmolality and suitable pH of fetal growth to maintain fetal quality. In addition, in order to achieve quality embryos, the use of frozen eggs and sperm in the laboratory can be effective in coordinating ovarian cycles and the readiness of the uterus for embryo transfer. Relying on the knowledge of experienced specialists in the Andarology and Embryology Laboratory of Histogenotech with ART laboratory equipment and specialized culture medium for freezing and thawing embryos, eggs and sperm, high survival results have been observed during the defrost process. It has had significant effects on successful in vitro fertilization in mice.Intracytoplasmic injection (ICSI)
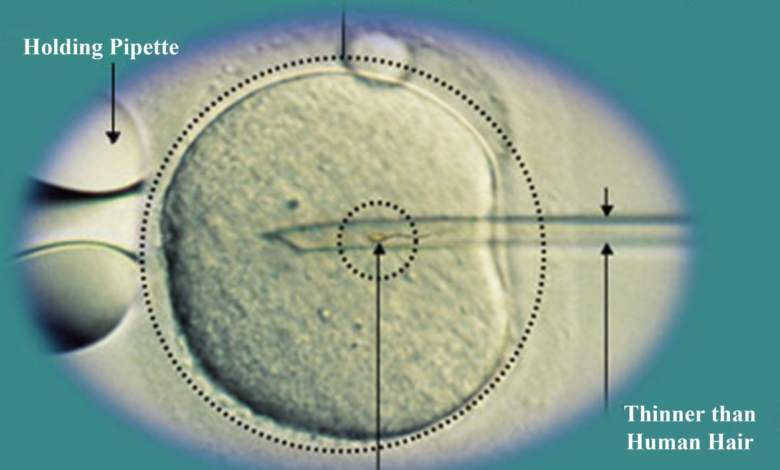
Sometimes sperm cannot penetrate the outer layer of the egg for various reasons. The outer layer of the egg may be thick or the surface receptors may be damaged or the sperm may not be able to swim. In these cases, a procedure called intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) is performed in conjunction with in vitro fertilization (IVF) to help fertilize the egg. During ICSI, a sperm is injected directly into the cytoplasm of the egg. There are two ways to fertilize an egg in the laboratory. Conventional method and ICSI. In traditional IVF, 50,000 or more floating sperm are placed next to the egg in a laboratory container. Fertilization occurs when one of the sperm enters the cytoplasm of an egg. In the ICSI process, a small needle called a micropipette is used to inject a sperm into the center of the egg. With traditional IVF, or ICSI, when fertilization occurs, the fertilized egg (now called the embryo) grows in the laboratory for 1 to 5 days before being transferred to the uterus.
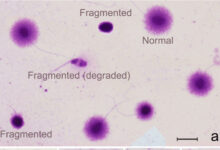
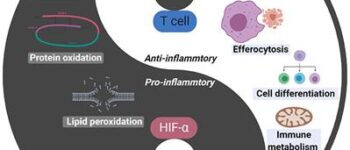
Evaluation of apoptosis in sperm, eggs and embryos
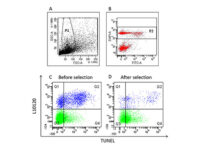
In order to achieve quality embryos, sperm and eggs with normal morphology, uniform cytoplasm and healthy DNA are needed. Various environmental factors including environmental stresses in assisted reproductive laboratories, in vitro cell culture and storage processes, freezing and thawing, and in vivo factors including genetic disorders in both males and females can lead to the development of defective embryos or gametes with damaged DNA. There are a variety of laboratory tests in Histogenotech to evaluate apoptosis in germ cells or fertilized embryos that can be effective in diagnosing this problem or designing research studies. These tests include the tunnel test, the annexin test, and the halosperm test.Evaluation of oxidative stress in ovarian, testicular, sperm, egg and fetal tissues
Measurement of oxidative stress and types of oxidants and oxygen oxidants (ROS) in ovarian and testicular tissues and in male and female germ cells is one of the most basic tests of research studies and knowing the amount of these compounds plays an essential role in infertility disorders. The presence of poor quality embryos in clinical laboratories can be due to the imbalance between antioxidant and oxidant compounds that can be measured by ELISA and flow cytometry in Histogenotech laboratories.Investigation of the concentration of antioxidants in tissues and cells
Antioxidant variables such as catalase (CAT), superoxide dismutase (SOD), GPX, GSH, TAC and oxidative stress variables including ROS and MDA on tissues and germ cells and embryos obtained in various studies have been studied. In fact, the measurement of these oxidative markers and antioxidants and creating research pathways in the study of various additives or herbal and chemical supplements to the culture medium of embryos and germ cells, can be considered in the treatment of ovarian and testicular diseases such as PCO and azoospermia.Fetal transfer to the uterus in a false pregnancy model
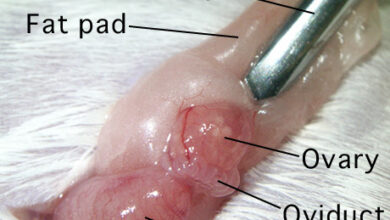
In order to transfer the embryo (embryo transfer) into the uterine tissue in the animal model, it is necessary to create a false pregnancy condition (Pseudo pregnancy). A false pregnancy, clinically called a pseudo pregnancy, assumes that you are expecting a baby when you are not actually carrying a baby. People with miscarriages have pregnancy symptoms but no fetus in the womb. Accordingly, sex hormones are high and the uterine wall is ready to accept the fetus, but there is no fetus. This condition is induced in animals in order to induce pregnancy by using a swab rotation in the vagina of the female animal or placing the female animal next to the male vasectomy animal. By doing this, the IVF embryos are ready to be transferred to the female animal’s body.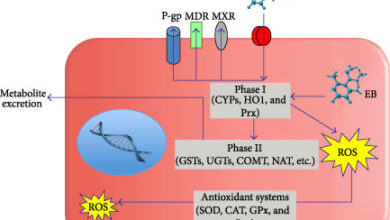
You may find the answer to your question
Frequently Asked Questions by Customers
In order to keep the embryo, egg or sperm for a short time in freezing conditions, the best way is to keep it at -80 ° C, but if you need to keep it longer, using liquid nitrogen at -196 ° C can lead to Preserve the genomic structure and morphology of cells. Thus, according to extensive studies, this maintenance method can be used for this purpose for many years by maintaining standard storage conditions. This long-term maintenance, sometimes up to 10 years, has been able to lead to the birth of healthy fetuses without any defects.
Molecular tests, including real-time PCR, ICC and Western Blot or function of some enzymes (ELISA), can be performed on fresh and frozen sperm, fresh eggs and frozen Fused with at least 1, fresh and frozen embryos with at least 1 for some tests. For this purpose, more specialized commercial kits were needed in small quantities, and in larger numbers, some tests can be studied manually.
Ovum, as a female germ cell, has different stages of nuclear maturation. Which, being enclosed inside a follicle and supported by follicular cells, develop through the stimulation of hormones (FSH, LH, Estrogen, Progesterone) during the sexual cycle. Depending on the size of the follicles and the number of rows of follicular cells around the egg, the follicles are divided into Primordial, Primary, Secondary, Pre-Antral, and Graf. On the other hand, the eggs inside the follicles are divided into GV, GVBD, MI, MII based on their nuclear maturation stage. In response to different phases of the sexual cycle at any time, some of the eggs can be in any of the stages.
Performing antioxidant tests or oxidative stress in eggs and fetuses with sperm and ovarian and testicular tissue are different due to the small number of fetal cells and eggs. To perform glutathione peroxidase (GPX), oxidative stress (ROS), and test for mitochondrial activity with JC dye, it is necessary to quantify the activity of the enzyme or other variables mentioned with fluorescent images with Image J software and by imaging. In the case of sperm, ovaries and testes, these assessments are performed by ELISA or flow cytometry or spectrofluorometric. Other tests such as superoxide dismutase, total antioxidant capacity or TAC in both cell and tissue can be performed by ELISA.
In order to develop transgenic animals, it is necessary to inject the desired gene fragment into the male pronuclear by microinjection (ICSI). Since the GFP reporter gene can be expressed alongside the target gene, it can indicate the success of vector function in the fetus. Thus, after embryonic cell proliferation, the target gene is expressed in all embryonic cells. The resulting embryo continues to grow by transferring the embryo to the fallopian tube or directly into the uterus to form a complete transgenic organism.
Due to the progress in the production of egg and embryo extraction kits, working with single cells can be done easily, so to perform Real time PCR technique and study gene expression can be expressed with a single egg or embryo by Single cell PCR method to evaluate the embryo and the egg. On the other hand, in order to perform ELISA tests and oxidative stress tests, these tests can be performed with at least 5 eggs and embryos.
Because many of the steps are almost the same with sperm, embryos and ova. Therefore, performing all steps such as sperm washing, freezing and thawing of sperm, examination of sperm parameters, intracytoplasmic injection of sperm, separation of motile sperm and good quality from other sperms, is similar to the human case. However, due to the high sensitivity of working with eggs and embryos, after learning all the steps of working with eggs and embryos of animals, it is necessary to do 6 months and one year internships in human laboratory and then work confidently with embryos and human eggs.
In this regard, the culture container used is made of polystyrene and with proper adhesion should be used. Thus, it is necessary to use HEPES culture medium in manual environments to create stable buffering conditions. In addition, in order to maintain the proper temperature, it is necessary to use the warm plate to maintain a temperature of 37°C during operation. Culture medium droplets with dimensions of 5 to 10 microliters, which can be increased up to 100 microliters, are used in a contracted manner with a specific rhythm from the beginning of the egg entering the container to the last drop as marked. Mineral Oil is used on the prepared droplets to prevent contamination when the lid of the culture dish is open under the microscope.