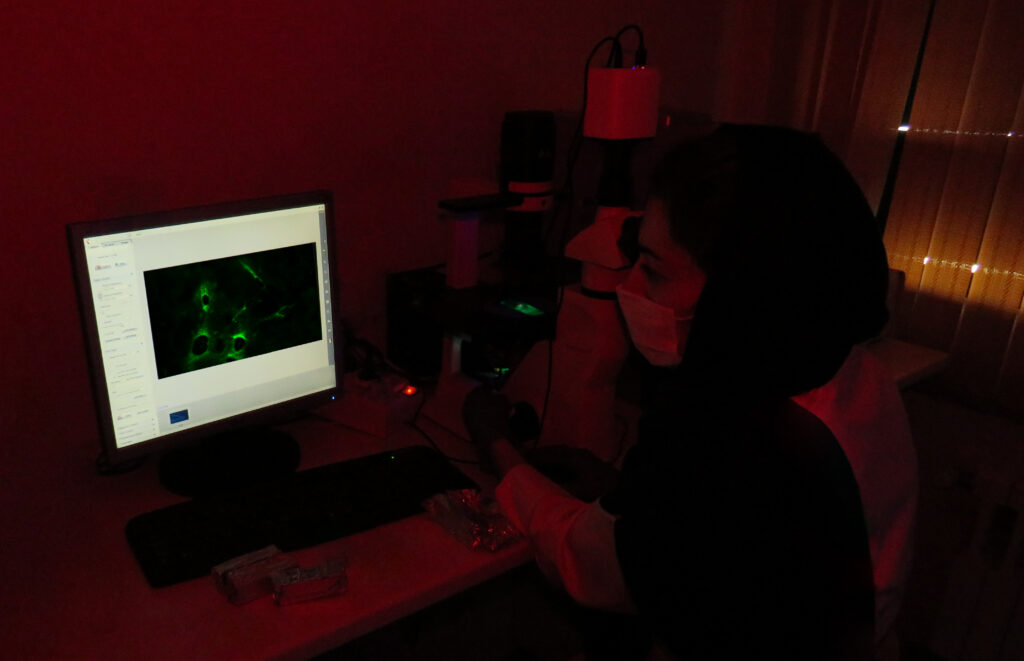
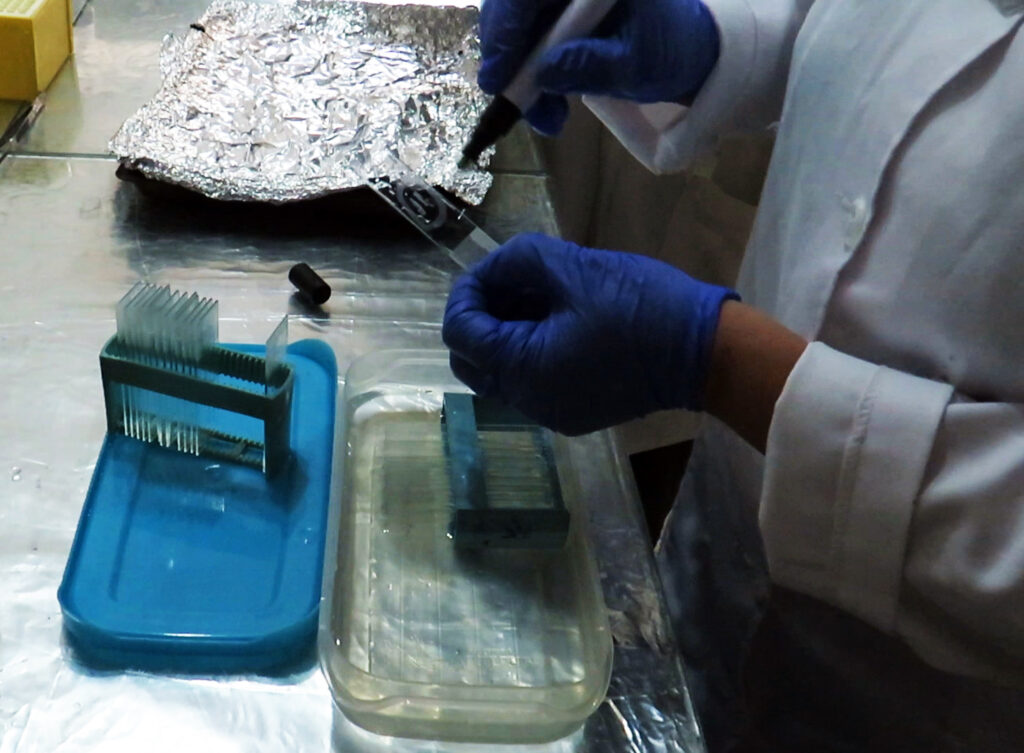
Immunohistochemistry IHC
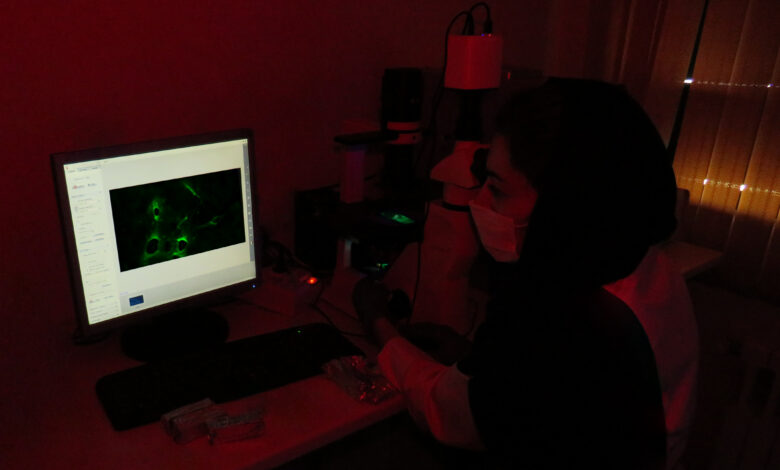
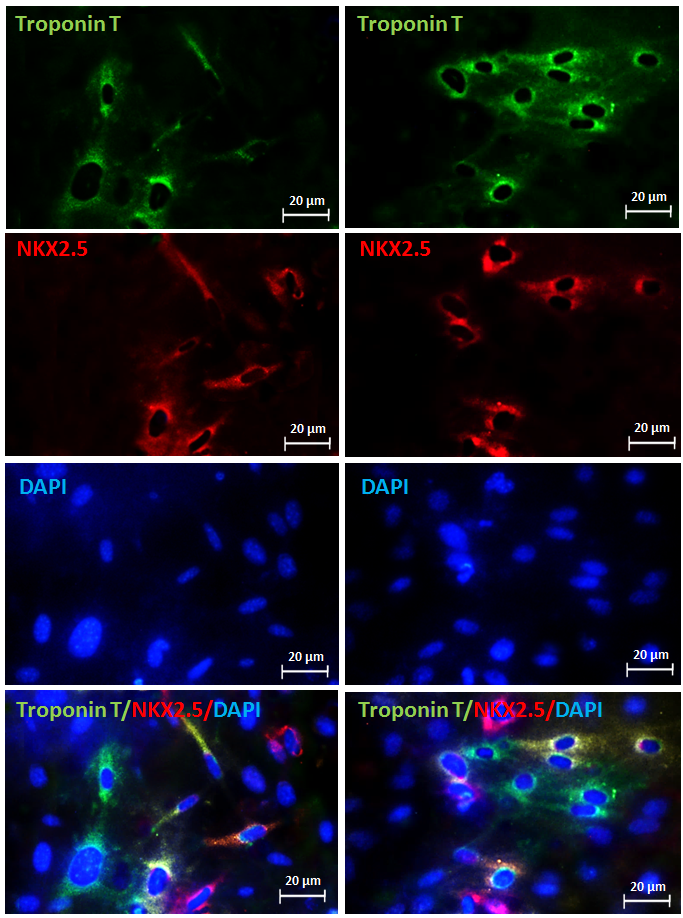
Immunohistochemistry IHC
Immunohistochemistry IHC is a method used to analyze protein expression in tissues. It is based on the specific binding of an antibody to its target epitope.
The use of immunological research methods in histopathology has led to a significant improvement in the microscopic diagnosis of neoplasms. Although histological analysis of hematoxylin and eosin stained tissue sections remains the core of the pathology, immunohistochemistry has become a powerful tool for pathologists.
Immunohistochemical staining is widely used in the diagnosis of abnormal cells such as cells in cancerous tumors. Specific molecular markers can identify specific cellular events such as proliferation or cell death (apoptosis). In addition, immunohistochemistry is used to determine the location and distribution of biomarkers and the expression of different proteins in different parts of biological tissues.
Typically, the goals of immunohistochemical studies have been to detect and identify the differentiation pathway of a particular tumor. But today this technique is used to identify and locate a variety of proteins in tissues and cells.
Immunohistochemical staining methods include the use of fluorescent-labeled antibodies (immunofluorescence) or enzyme-labeled antibodies (immunoperoxidase) that are used to identify proteins and other molecules in the tissue.
In pathological diagnoses, immunoperoxidase methods are widely used to obtain additional information that is not available by H&E staining and light microscopy.
Immunohistochemistry steps:
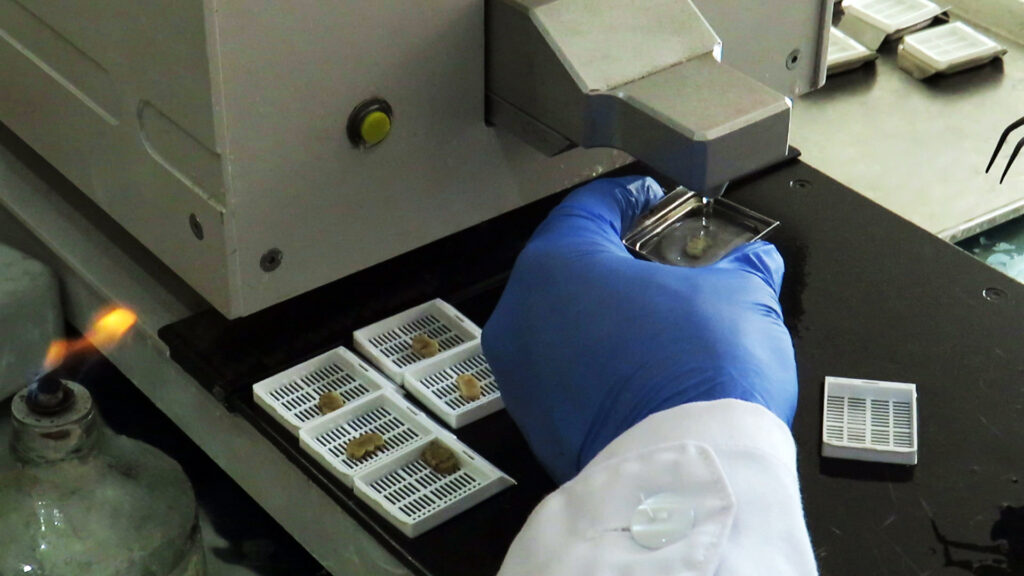
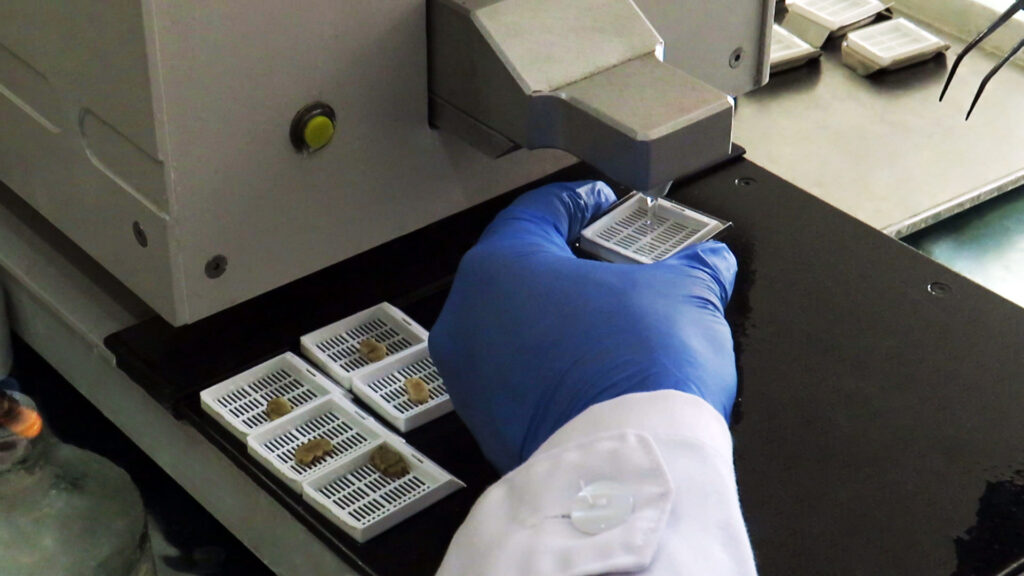
1: Fixing the desired tissue by immersing it for 24 to 48 hours in 10% formalin
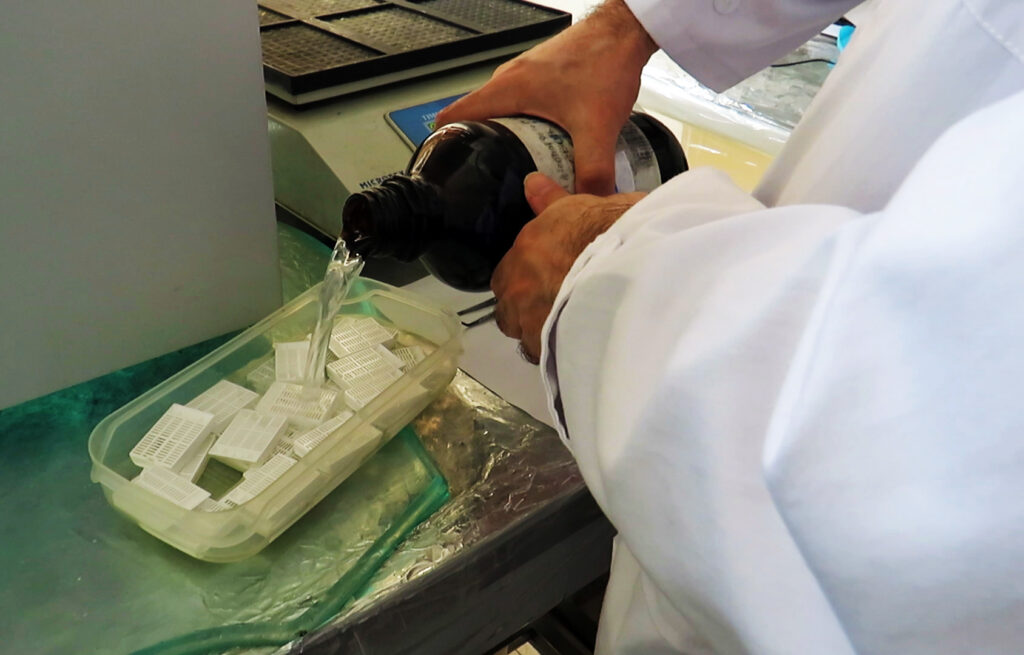
2: Dehydration step: Incubate the tissues in ethanol 70%, 80% , 95% for 45 minutes each, and 3 times in 100% ethanol for 100 minutes each time.
After dehydration, to clarify and wash the materials of the previous step,
3: Incubate the tissues for one hour each for transparency in xylene one and two.
4: Immerse the tissues in paraffin one, two and three each for one hour.
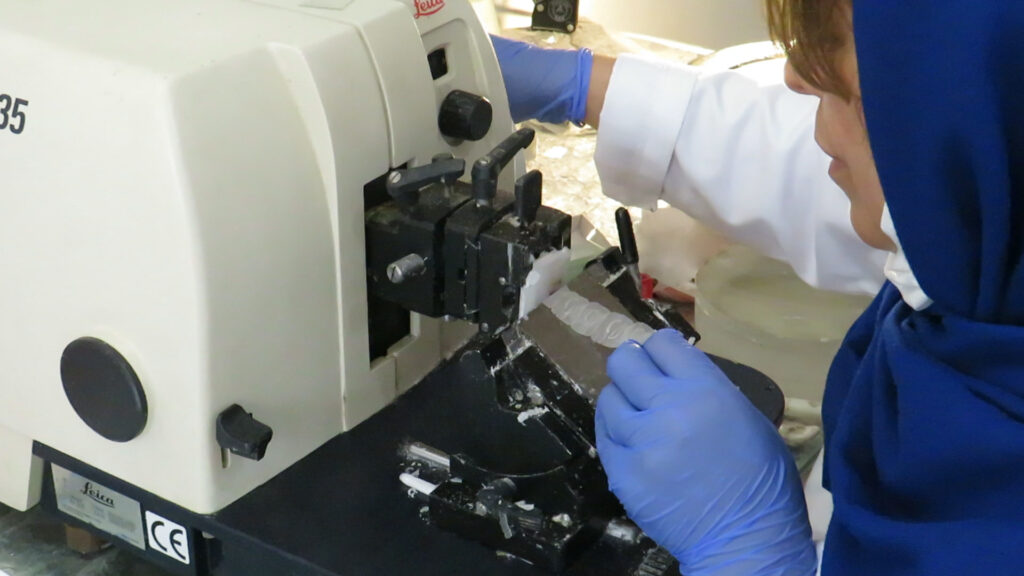
5: Place the tissues in paraffin blocks and then cut with a microtome and transfer to the slide.
6: Deparaffinization of tissues: Place the slides in xylene solution 1 and 2 each for 5 minutes, then insert the slides twice and each time for 3 minutes in 100% ethanol and then once for 3 minutes each Put one of the concentrations of 95, 70 and 50 ethanol. Then dry the slides overnight at room temperature.
7: In order to block cellular peroxidase activity, the slides are incubated in a solution of methanol containing 3% H2O2 for 10 minutes. Then wash 2 times and each time for 5 minutes with PBS.
8: To expose antigen epitopes, place the slides in a container and pour citrate buffer on it and heat the container for 95 minutes at 95 to 100 ° C. Then let the dish cool for 20 minutes at room temperature.
9: Rinse the slides twice, each time for 5 minutes with PBS.
10: Pour a suitable amount of blocking buffer (e.g. 10% fetal bovine serum in PBS) on each slide and then leave it at room temperature for one hour and then rinse with PBS.
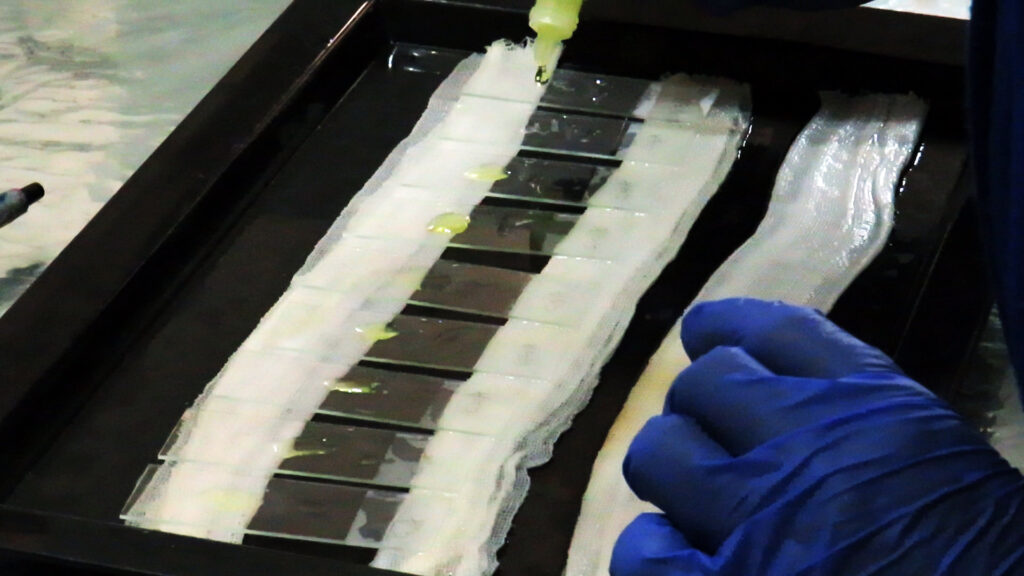
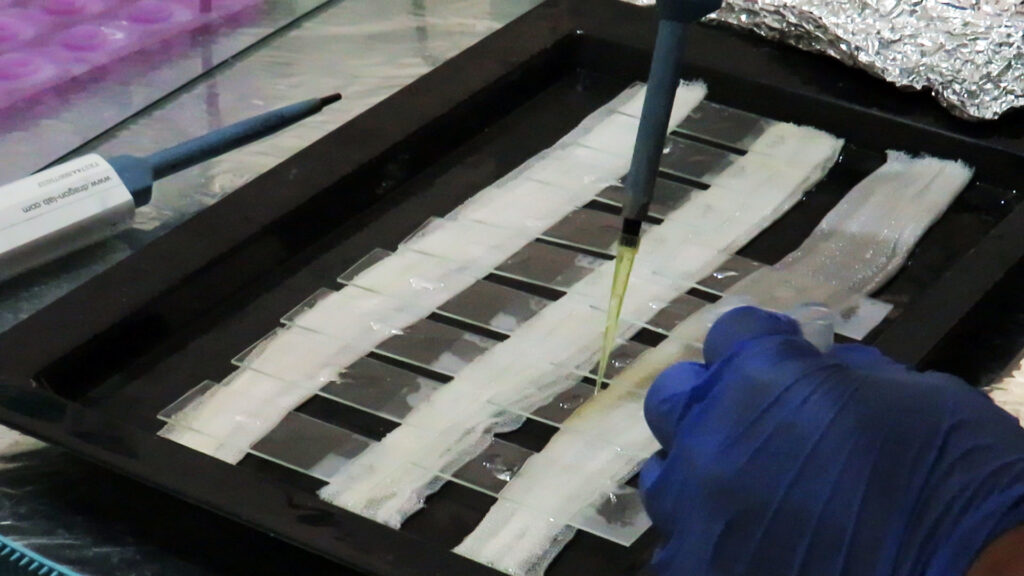
11: Pour a suitable amount of diluted primary antibody on the tissues and leave it at room temperature for one hour. Then wash twice with PBS and five minutes each time.
12: Pour a suitable amount of diluted secondary antibody on each slide and leave it at room temperature for 30 minutes. Then wash the slides twice with PBS and each time for 5 minutes.
13: Pour a good amount of diluted Sav-HRP on the tissues and leave in the dark for 30 minutes. Then rinse the slides twice with PBS for 5 minutes each time.
14: Pour a suitable amount of DAB solution on each tissue and incubate for 5 minutes and then wash 3 times with PBS.
15: Put the slides in hematoxylin for two minutes and then rinse with water.
16: Place the slides in 95% and 100% ethanol twice for 5 minutes each.
17: Place the slides inside the xylene for transparency and then mount the slides.
Related services: Histology, tissue engineering and pathology staining