nanoparticle-synthesis
Synthesis and production of metal nanoparticles, polymers and nanoemulsions
Some of the synthesized Nano particles in the Histogenotech nano-technology center are as follows
- Metal Nano particles
- Ag Nano particles
- Zn Nano Particles
- Fe Nano Particles
- Polymeric Nano particles
- Alginate Nano particles
- Liposomal Nano Particles
- Nano Chitosan
- Nano Emulsions
- Nano Micelle

Histogenotech research center is very proud to deliver scientific and technical supports on synthesis and characterization of different types of Polymeric, Metal, Ceramic and lipid base nano- particles using well-equipped laboratories.
Nano materials have wide range of applications and quality improvement in environmental, medical, pharmaceutical, food, Diagnostic and therapeutic, cosmetics, agriculture, energy, textile and electronic industries. Undoubtedly, these materials are more efficient compared to non-nanomaterials. Nanotechnology is expected to succession of sciences and overcome diseases and contaminations using nanoscale materials and particles.

Nanoparticles And Nanomaterials Synthesis And Characterization In Histogenotech
Nanoparticles and nanomaterials Synthesis and Characterization inHistogenotech

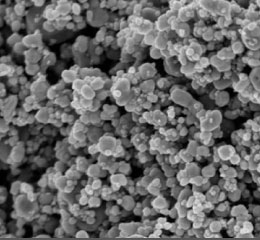
Metal nanoparticle
Metal nanoparticles (such as gold, silver, copper, metal, etc.) are a metal core composed of metallic minerals or metal oxide, which is usually coated with a shell of organic material, mineral material or metal oxide. These nanoparticles are widely used in research and industrial activities due to their unique optical, electrical and magnetic properties. For example, optical properties of metal nanomaterial has attracted much interest, recently because of the generation of very strong electric fields in the proximity of their surfaces. Recent developments in Nanotechnology enables to produce a variety of cost effective and modified consumer products such as creams, shampoos, clothing, and plastic containers. Histogenotech research center serves synthesize and characterization of these nanomaterials by using advanced equipment and experienced specialists.
Ag Nanoparticles
The antibacterial activity of silver has long been known and has found a variety of applications. Silver can continually release silver ions, which may be considered the mechanism of killing microbes. Owing to electrostatic attraction and affinity to sulfur proteins, silver ions can adhere to the cell wall and cytoplasmic membrane and finally lead to bacterial disruption. Silver nano particles have been widely used as antibacterial agents, in industrial, household, and healthcare-related products, in consumer products, medical device coatings, optical sensors, and cosmetics, in the pharmaceutical industry, the food industry, in diagnostics, orthopedics, drug delivery, as anticancer agents, and biosensors for cancer diagnosis, medical imaging, and coating of vascular prostheses because of to their peculiar properties. Histogenotech Company offers synthesizing and characterization services for various types of silver nanoparticles with the highest level of expertise and support.
Zn Nanoparticles
Zink oxide (ZnO) is one of the most widely used metal oxide/metal nanoparticles to synthesize biological nanoparticles for medical and pharmaceutical purposes. Nano-sized ZnO exhibits varying morphologies and shows significant antibacterial activity over a wide spectrum of bacterial species explored by a large body of researchers. ZnO holds a unique optical, chemical sensing, semiconducting, electric conductivity, and piezoelectric properties. Zink oxide crystalyzes can be found in cubic and hexagonal wurtzite (Wz) structure but using of hexagonal ZnO is more common due to its ambient stability. Antibiotic-resistant infections caused by Gram-negative pathogens pose a major threat to human health. Zink oxide nano-particle is significantly reduced the pathogen generations and phenotype resistance and minimizing unnecessary prescribing and overprescribing of antibiotics. ZnO is a bio-safe material without any major negative side effects to human. Histogenotech Company provides nanomaterials synthesizing and characterization services for students and research scholars with the highest level of expertise and support.
Iron Oxide Nanoparticles
Magnetic NPs such as Iron-oxide nanoparticles have many unique magnetic properties such as superparamagnetic, high coercively, low Curie temperature, high magnetic susceptibility, etc. Magnetic NPs are of great interest for researchers from a broad range of disciplines, including magnetic fluids, data storage, catalysis, and bio-applications. However, these nano-sized iron oxide particles are faced with several weaknesses such as inherent instability in the presence of air (oxidation), insbility to metabolize in the body and removal from the body. Therefore, permeation of high concentrations of iron ions to the mitochondrial wall and nucleus can be caused toxicity within the body. Thus, iron cores are coated with organic/ inorganic polymers in order to minimize these destructive features. Moreover, it can be enhanced the biocompatibility of these particles and allows the various ligands including antibodies to attach their surface.The cells or biomolecules which are non-magnetic in nature can be attached to magnetic responsive beads and thus manipulated using an external magnetic field and the cells are directed by means of a magnetic field gradient towards certain tissue targets. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles have found widespread applications in the biomedical field compared to the other magnetic nanoparticles. Nanoscale iron particles are sub-micrometer particles of iron metal. They are highly reactive because of their large surface area and can be rapidly oxidized to form free iron ions in the presence of oxygen and water. They have been used widely in medical and laboratory applications and have also been studied for remediation of contaminated industrial sites with chlorinated organic compounds. Histogenotech research center offers synthesize and characterization of nano-structured materials using the most advanced laboratory equipment.
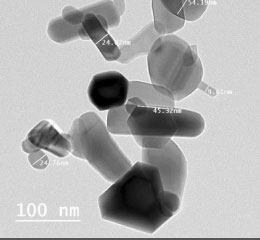
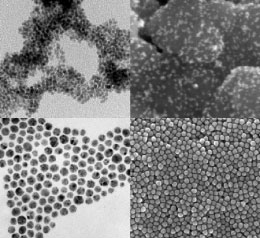
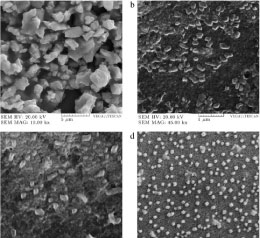
Polymeric nanoparticles
Polymeric nanoparticles (NPs) have attracted considerable interest over recent years due to their properties resulting from their small size range (1 to 1000 nm). They can be loaded with active compounds entrapped within or surface-adsorbed onto the polymeric core. Advantages of polymeric NPs as drug carriers include their potential use for controlled release, the ability to protect drug and other molecules with biological activity against the environment, improve their bioavailability and therapeutic index. Polymeric nanoparticles causes a reinforcement in polymeric network and higher rigidity. The various biodegradable polymers commonly used in the fabrication of polymeric nanoparticles include poly(lactide) (PLA), poly(lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA) copolymers, poly (ɛ-caprolactone) (PCL), and poly(amino acids) and also some natural polymers like alginate, chitosan, gelatin, and albumin. The polymeric nano-revolution in medicine and medical applications is an exciting prospect as it boasts the potential to transform the conceivable solutions of current cancer, neurological disorders and cardiovascular diseases and biological challenges. These biocompatible, biodegradable and low toxic nanomaterials hold great promise in delivery and controlled release of the drugs. Histogenotech research center offers synthesize and characterization of polymeric nano materials using the most advanced laboratory equipment.
Alginate nanoparticles
Alginates are polysaccharides found in brown seaweeds, and the most abundant marine biopolymer and, after cellulose, the most abundant biopolymer in the world. Alginic acid and sodium and potassium alginates have emerged as one of the most extensively explored mucoadhesive biomaterials owing to very good cytocompatibility and biocompatibility, biodegradation, sol-gel transition properties, and chemical versatility that make possible further development to modify their properties. Alginate nanoparticles form a viscous gum in presence of water which have known as one of the most applicable biomaterials used for drug delivery. Histogenotech research center offers synthesize and characterization of nano-alginate coating materials with an analysis certification for all research groups and industries.
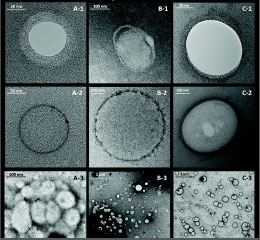
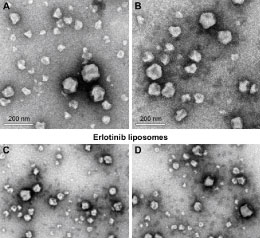
Liposomal Nanoparticles
Liposomes are verified as a well-established and suitable candidate for drug delivery and cancer treatment because of their ability to store drugs with different physical and chemical characteristics. They are similar to biological membranes and are composed of at least bilayer phospholipids, which are amphipathic and are characterized by having a lipophilic tail and hydrophilic head on the same molecule. Moreover, capability of controlled drug release, biocompability, biodegradability and minimizing drug side effects are the other attractive liposomes properties. For example, cationic liposomes are one of the most powerful non-viral vectors for gene therapy applications. Moreover, Liposomes can increase the sensitivity, specificity, and durability of anti-malignant cell agents in the body and provide remarkable benefits to be applied in nano-medicines. Therefore, a great revolution in drug delivery systems is expected by using liposomes. Lipid bacteria can also be used to prepare liposomes. The ease of access to microorganisms and their ability to grow on various substrates, make bacterial lipids appropriate candidates for liposome preparation. Histogenotech research center has extensive technical knowledge and skills to support the projects on production of nano-materials.
Chitosan nanoparticles
Chitosan, a biocompatible natural polysaccharide is frequently used for production of nano-particles, nano-coating and nano-carriers. Chitin is the most abundant biopolymer in nature after cellulose. Chitin is generally found as ordered crystalline microfibrils in the structural component of crustaceans and insects, and is also found in the cells of fungi and microorganisms. Chitin and chitosan are both fully biocompatible and biodegradable natural amino polysaccharides and can be used as antibacterial and antifungal agent. Chitosan and its derivatives are extensively applicable in medical and pharmaceutical fields due to their competitive biological properties like biocompatibility, biodegradability, nontoxicity, and analgesic, antitumor, hemostatic, hypocholesterolemic, antimicrobial, and antioxidant properties These properties are very advantageous in biomedical applications of tissue engineering, wound healing, excipients for drug delivery, and gene delivery. Histogenotech research center offers synthesize and characterization of chitosan nano-materials using the most advanced laboratory equipment.
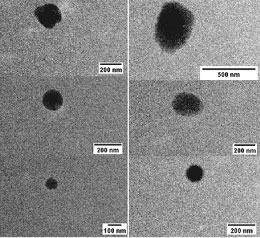
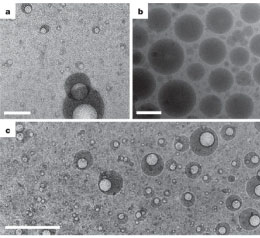
Nano-emulsions
Nano-emulsion is an important and valuable tool in the nano-technological field designed for clinical and therapeutic application. Nano-emulsions are colloidal particulate systems in the submicron size range consisting of two heterogeneous liquids such as oil and water. Nano-emulsions are kinetically stable and thermodynamically unstable colloidal liquid-in-liquid dispersions with droplet sizes in the order of 20–500 nm. Emulsions in this size range can appear translucent or optically clear if the average oil droplet size is < 100 nm because of no scattering light withwithin droplets. Furthermore, nano-emulsions are conferred with kinetic stability as there is no gravitational separation and droplet aggregation due to the reduced attractive force between the small sized droplets. Therefore, they have many advantages over conventional emulsions, including optical transparency, high kinetic and thermodynamic stability, environmental compatibility and biodegradability, large surface area and ease of preparation. Hence, they have the added benefit of aiding in drug penetration to the epithelial mucosol layers, controlled drug delievery, chemotraphy and cancer treatment. Histogenotech research center provides facilities and services for various types of nano-emulsions in laboratory, semi-industrial and industrial scales.
Nano-micelle
Nano-micelles have been widely used as drug carriers for a long time, compared to other nano particles. Nano-micelles are colloidal constructs composed of amphiphilic monomers and are consisted of a small hydrophobic head and a long hydrophilic tail. The hydrophobic core interacts with hydrophobic drugs/agents, while the hydrophilic tail helps surrounding with water and enhances solubility. Micelles have been commonly employed as drug delivery carriers for a series of different molecules, including low molecular mass hydrophobic drugs, proteins, and genes because of its valuable properties. One of the most well-known example is the transfer of water-soluble curcumin, which is normally insoluble in water. The low solubility of curcumin in salivary fluid, poor stability in gastric and intestinal fluids, slight cell absorption, high metabolism and several side effects resulting in limited curcumin applications. Encapsulation of curcumin with nano-micelles significantly improved the solubility and stability of curcumin. Histogenotech nano-technology center has extensive research experience in nanomaterial synthesis, characterization and development of nano-delivery systems for herbal medicine and extracts to increase their effectiveness.
Metal nanoparticles (such as gold, silver, copper, metal, etc.) are a metal core composed of metallic minerals or metal oxide, which is usually coated with a shell of organic material, mineral material or metal oxide. These nanoparticles are widely used in research and industrial activities due to their unique optical, electrical and magnetic properties. For example, optical properties of metal nanomaterial has attracted much interest, recently because of the generation of very strong electric fields in the proximity of their surfaces. Recent developments in Nanotechnology enables to produce a variety of cost effective and modified consumer products such as creams, shampoos, clothing, and plastic containers. Histogenotech research center serves synthesize and characterization of these nanomaterials by using advanced equipment and experienced specialists.
The antibacterial activity of silver has long been known and has found a variety of applications. Silver can continually release silver ions, which may be considered the mechanism of killing microbes. Owing to electrostatic attraction and affinity to sulfur proteins, silver ions can adhere to the cell wall and cytoplasmic membrane and finally lead to bacterial disruption. Silver nano particles have been widely used as antibacterial agents, in industrial, household, and healthcare-related products, in consumer products, medical device coatings, optical sensors, and cosmetics, in the pharmaceutical industry, the food industry, in diagnostics, orthopedics, drug delivery, as anticancer agents, and biosensors for cancer diagnosis, medical imaging, and coating of vascular prostheses because of to their peculiar properties. Histogenotech Company offers synthesizing and characterization services for various types of silver nanoparticles with the highest level of expertise and support.
Zink oxide (ZnO) is one of the most widely used metal oxide/metal nanoparticles to synthesize biological nanoparticles for medical and pharmaceutical purposes. Nano-sized ZnO exhibits varying morphologies and shows significant antibacterial activity over a wide spectrum of bacterial species explored by a large body of researchers. ZnO holds a unique optical, chemical sensing, semiconducting, electric conductivity, and piezoelectric properties. Zink oxide crystalyzes can be found in cubic and hexagonal wurtzite (Wz) structure but using of hexagonal ZnO is more common due to its ambient stability. Antibiotic-resistant infections caused by Gram-negative pathogens pose a major threat to human health. Zink oxide nano-particle is significantly reduced the pathogen generations and phenotype resistance and minimizing unnecessary prescribing and overprescribing of antibiotics. ZnO is a bio-safe material without any major negative side effects to human. Histogenotech Company provides nanomaterials synthesizing and characterization services for students and research scholars with the highest level of expertise and support.
Magnetic NPs such as Iron-oxide nanoparticles have many unique magnetic properties such as superparamagnetic, high coercively, low Curie temperature, high magnetic susceptibility, etc. Magnetic NPs are of great interest for researchers from a broad range of disciplines, including magnetic fluids, data storage, catalysis, and bio-applications. However, these nano-sized iron oxide particles are faced with several weaknesses such as inherent instability in the presence of air (oxidation), insbility to metabolize in the body and removal from the body. Therefore, permeation of high concentrations of iron ions to the mitochondrial wall and nucleus can be caused toxicity within the body. Thus, iron cores are coated with organic/ inorganic polymers in order to minimize these destructive features. Moreover, it can be enhanced the biocompatibility of these particles and allows the various ligands including antibodies to attach their surface.
The cells or biomolecules which are non-magnetic in nature can be attached to magnetic responsive beads and thus manipulated using an external magnetic field and the cells are directed by means of a magnetic field gradient towards certain tissue targets. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles have found widespread applications in the biomedical field compared to the other magnetic nanoparticles. Nanoscale iron particles are sub-micrometer particles of iron metal. They are highly reactive because of their large surface area and can be rapidly oxidized to form free iron ions in the presence of oxygen and water. They have been used widely in medical and laboratory applications and have also been studied for remediation of contaminated industrial sites with chlorinated organic compounds. Histogenotech research center offers synthesize and characterization of nano-structured materials using the most advanced laboratory equipment.
Polymeric nanoparticles (NPs) have attracted considerable interest over recent years due to their properties resulting from their small size range (1 to 1000 nm). They can be loaded with active compounds entrapped within or surface-adsorbed onto the polymeric core. Advantages of polymeric NPs as drug carriers include their potential use for controlled release, the ability to protect drug and other molecules with biological activity against the environment, improve their bioavailability and therapeutic index. Polymeric nanoparticles causes a reinforcement in polymeric network and higher rigidity. The various biodegradable polymers commonly used in the fabrication of polymeric nanoparticles include poly(lactide) (PLA), poly(lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA) copolymers, poly (ɛ-caprolactone) (PCL), and poly(amino acids) and also some natural polymers like alginate, chitosan, gelatin, and albumin. The polymeric nano-revolution in medicine and medical applications is an exciting prospect as it boasts the potential to transform the conceivable solutions of current cancer, neurological disorders and cardiovascular diseases and biological challenges. These biocompatible, biodegradable and low toxic nanomaterials hold great promise in delivery and controlled release of the drugs. Histogenotech research center offers synthesize and characterization of polymeric nano materials using the most advanced laboratory equipment.
Alginates are polysaccharides found in brown seaweeds, and the most abundant marine biopolymer and, after cellulose, the most abundant biopolymer in the world. Alginic acid and sodium and potassium alginates have emerged as one of the most extensively explored mucoadhesive biomaterials owing to very good cytocompatibility and biocompatibility, biodegradation, sol-gel transition properties, and chemical versatility that make possible further development to modify their properties. Alginate nanoparticles form a viscous gum in presence of water which have known as one of the most applicable biomaterials used for drug delivery. Histogenotech research center offers synthesize and characterization of nano-alginate coating materials with an analysis certification for all research groups and industries.
Liposomes are verified as a well-established and suitable candidate for drug delivery and cancer treatment because of their ability to store drugs with different physical and chemical characteristics. They are similar to biological membranes and are composed of at least bilayer phospholipids, which are amphipathic and are characterized by having a lipophilic tail and hydrophilic head on the same molecule. Moreover, capability of controlled drug release, biocompability, biodegradability and minimizing drug side effects are the other attractive liposomes properties. For example, cationic liposomes are one of the most powerful non-viral vectors for gene therapy applications. Moreover, Liposomes can increase the sensitivity, specificity, and durability of anti-malignant cell agents in the body and provide remarkable benefits to be applied in nano-medicines. Therefore, a great revolution in drug delivery systems is expected by using liposomes. Lipid bacteria can also be used to prepare liposomes. The ease of access to microorganisms and their ability to grow on various substrates, make bacterial lipids appropriate candidates for liposome preparation. Histogenotech research center has extensive technical knowledge and skills to support the projects on production of nano-materials.
Chitosan, a biocompatible natural polysaccharide is frequently used for production of nano-particles, nano-coating and nano-carriers. Chitin is the most abundant biopolymer in nature after cellulose. Chitin is generally found as ordered crystalline microfibrils in the structural component of crustaceans and insects, and is also found in the cells of fungi and microorganisms. Chitin and chitosan are both fully biocompatible and biodegradable natural amino polysaccharides and can be used as antibacterial and antifungal agent. Chitosan and its derivatives are extensively applicable in medical and pharmaceutical fields due to their competitive biological properties like biocompatibility, biodegradability, nontoxicity, and analgesic, antitumor, hemostatic, hypocholesterolemic, antimicrobial, and antioxidant properties These properties are very advantageous in biomedical applications of tissue engineering, wound healing, excipients for drug delivery, and gene delivery. Histogenotech research center offers synthesize and characterization of chitosan nano-materials using the most advanced laboratory equipment.
Nano-emulsion is an important and valuable tool in the nano-technological field designed for clinical and therapeutic application. Nano-emulsions are colloidal particulate systems in the submicron size range consisting of two heterogeneous liquids such as oil and water. Nano-emulsions are kinetically stable and thermodynamically unstable colloidal liquid-in-liquid dispersions with droplet sizes in the order of 20–500 nm. Emulsions in this size range can appear translucent or optically clear if the average oil droplet size is < 100 nm because of no scattering light withwithin droplets. Furthermore, nano-emulsions are conferred with kinetic stability as there is no gravitational separation and droplet aggregation due to the reduced attractive force between the small sized droplets. Therefore, they have many advantages over conventional emulsions, including optical transparency, high kinetic and thermodynamic stability, environmental compatibility and biodegradability, large surface area and ease of preparation. Hence, they have the added benefit of aiding in drug penetration to the epithelial mucosol layers, controlled drug delievery, chemotraphy and cancer treatment. Histogenotech research center provides facilities and services for various types of nano-emulsions in laboratory, semi-industrial and industrial scales.
Nano-micelles have been widely used as drug carriers for a long time, compared to other nano particles. Nano-micelles are colloidal constructs composed of amphiphilic monomers and are consisted of a small hydrophobic head and a long hydrophilic tail. The hydrophobic core interacts with hydrophobic drugs/agents, while the hydrophilic tail helps surrounding with water and enhances solubility. Micelles have been commonly employed as drug delivery carriers for a series of different molecules, including low molecular mass hydrophobic drugs, proteins, and genes because of its valuable properties. One of the most well-known example is the transfer of water-soluble curcumin, which is normally insoluble in water. The low solubility of curcumin in salivary fluid, poor stability in gastric and intestinal fluids, slight cell absorption, high metabolism and several side effects resulting in limited curcumin applications. Encapsulation of curcumin with nano-micelles significantly improved the solubility and stability of curcumin. Histogenotech nano-technology center has extensive research experience in nanomaterial synthesis, characterization and development of nano-delivery systems for herbal medicine and extracts to increase their effectiveness.
YOU MAY FIND THE ANSWER TO YOUR QUESTION
Frequently Asked Questions By Customers
The DLS test is used to check the average size of synthesized nanoparticles. In this test, nanoparticles are passed through a section and the size of the nanoparticles is checked. The common size of metal nanoparticles is below 100 nm and for nano-carriers up to about 300 nm in the normal range.
Yes, synthesis conditions can determine the size of nanoparticles. Whit the higher amount of energy and the longer exposure time can produce the smaller the size of the particles.
The answer of this question is according to the researcher needs, but in general both metal nanoparticles and polymer nanoparticles can be used in biological studies, but there are different parameters to choose from including, the active ingredient, the model in which the active ingredient is to be used in the animal (topical, gastrointestinal, respiratory, ocular, etc.)
In general, synthesized nanoparticles should be examined in terms of several parameters:
– Morphological shape of particles can determine by electron microscopy.
– Particle size that is checked by DLS device.
– Particle charge which is done by zeta sizer.
– The connection status of the carrier and the active substance that can be checked by FTIR test.
These parameters are the minimum parameters required in the study of synthesized nanoparticles.
Yes, in general, emulsions are a combination of two incompatible substances such as water and oil, which are forcibly combined by a process of mechanical energy. Nanoparticles can also be synthesized from emulsions, known as nano-emulsions.
Synthesized nanoparticles can have a negative or positive charge, which is important in their absorption in cells, tissues or in different environments. In general, it can be said that nanoparticles are stable in the range of -30 to +30 electric charge.
In general, microscopic observation techniques can be examined as follows:
– Fe-SEM microscope can be used to observe fine particles with the best resolution and in three dimensions.
– SEM microscope with a resolution of 5 times less than Fe-SEM in three dimensions.
– E-SEM microscope, which is three-dimensional and can often be used for liquid samples.
– TEM microscope which is two-dimensional and has a higher resolution than SEM microscopes.
The answer to this question should be done according to the researcher needs, but in general there are different parameters to choose from, for example, the active ingredient to be used, and the model in which the active ingredient is to be used in the animal (topical, digestive, and respiratory, ocular, etc.) and so on.
شاید جواب سوال خود را بیابید
سوال های متداول مشتریان
بله، شرایط سنتز می تواند تعیین کننده سایز نانوذرات باشد. هر چه میزان انرژی وارده و مدت زمان ایجاد انرژی زیاد باشد سایز ذرات سنتز شده را میتوان کوچکتر مشاهده نمود.
پاسخ به این سوال با توجه به نیازهای شما باید انجام پذیرد، اما به طور کلی هم از نانوذرات فلزی و هم از نانوذرات پلیمری میتوان در مطالعات بیولوژیکی استفاده نمود اما پارامترهای متفاوتی برای انتخاب وجود دارد برای مثال ماده موثره ای که قرار است استفاده شود، مدلی که قرار است ماده موثره در حیوان استفاده شود (موضعی، گوارشی، تنفسی، چشمی و …..)
به طور کلی نانوذرات سنتز شده باید از لحاظ چند پارامتر بررسی شوند:
– شکل مرفولوژیک ذرات که توسط میکروسکوپ الکترونی انجام میشود.
– سایز ذرات که توسط دستگاه DLS بررسی میشود.
– بار ذرات که توسط بررسی زتا انجام میپذیرد.
– وضعیت اتصال حامل و ماده موثره که با تست FTIR قابل بررسی است.
این موارد حداقل پارامترهای مورد نیاز در بررسی نانوذرات سنتز شده می باشد.
تست DLS، برای بررسی متوسط اندازه ی نانوذرات سنتز شده می باشد. در این تست نانو ذرات از یک مقطع عبور داده میشوند و اندازه نانوذرات آن بررسی میگردد. این اندازه به صورت متوسط در نانوذرات زیر 100 نانومتر و در نانوپوشش ها تا حدود 300 نانومتر در رنج نرمال می باشد.
نانوذرات سنتز شده میتوانند بار منفی و یا مثبت داشته باشند که در جذب آنها در سلول ها، بافت ها و یا به صورت کلی محیط های متفاوت دارای اهمیت است. در کل میتوان گفت نانوذرات در بازه 30- تا 30+ بار الکتریکی دارای پایداری می باشند.
به طور کلی میتوان تکنیک های مشاهده میکروسکوپی را به شکل زیر بررسی نمود:
– میکروسکوپ Fe-SEM برای مشاهده ریز ذرات با بهترین قدرت تفکیک و به صورت سه بعدی قابل استفاده می باشد.
– میکروسکوپ SEM که قدرت تفکیک آن 5 برابر کمتر از Fe-SEM به صورت سه بعدی می باشد. – میکروسکوپ E-SEM که به صورت سه بعدی بوده و اغلب برای نمونه های مایع قابل استفاده میشود. – میکروسکوپ TEM که به صورت دو بعدی بوده و قدرت تفکیک بالاتری از میکروسکوپ های SEM دارد.
پاسخ به این سوال با توجه به نیازهای شما باید انجام پذیرد، اما به طور کلی پارامترهای متفاوتی برای انتخاب وجود دارد برای مثال ماده موثره ای که قرار است استفاده شود، مدلی که قرار است ماده موثره در حیوان استفاده شود (موضعی، گوارشی، تنفسی، چشمی و …..) و بسیاری از پارامترهای دیگر که در بررسی تخصصی کار مشخص میگردد.
بله در کل امولسیون ها ترکیبی از دوماده غیر قابل ترکیب مثل آب و روغن می باشند که با فرآیند انرژی مکانیکی به اجبار با هم ترکیب میشوند. از امولسیون ها میتوان نانوذرات نیز سنتز نمود که تحت عنوان نانوامولسیون ها شناخته میشوند.






















