Extraction, essential oils and active ingredients of medicinal plants
Some of the techniques presented in Histogenotech
- Soxhlet
- Infusion
- Maceration
- Digestion
- Decoction
- Percolation
- Ultrasonic
- Microwave assist

Due to the importance of natural products, the consumption of various extracts and essential oils obtained from medicinal plants is very crucial today. The global organization’s emphasis on the gradual replacement of natural active ingredients with chemical active ingredients in the food, health, cosmetics, and especially pharmaceutical industries has led various countries to invest in and plan for the production of industrial herbal products.

Plant Studies Services
Maceration method
One of the most common methods of extracting from plants is the use of maceration method. This temperature independent extraction method, which is based on mixing and proximity of solvent and plant seems ideal for biological studies of plant products. In recent years, herbal medicine unit of Histogenotech with the creation of plant herbarium has produced more than 70 types of plant extracts from different plants. Also, services related to maceration method are perform in Histogenotech as a common method.



Infusion method
The infusion extraction process is almost similar to the maceration method. This method is suitable for extracting active components that are easily soluble, but this method is less popular than the conventional method such as maceration. However, the Histogenotech Medicinal Plants Unit, with the help of its specialists, also provides infusion services.


Digestion
The digestion method is mostly used to extract substances that do not dissolve easily in the solvent and are not sensitive to temperatures of 60-50 ° C. This extraction method is also used in the Histogenotech Company.
Decoction method
This method, which uses boiling temperature, is used for water-based extraction and is used for active ingredients that are resistant to boiling temperature. In this method, the temperature changes gradually until it reaches the boiling point. As with other extraction methods, the Histogenotech herbal medicine unit is ready to provide services in this way.
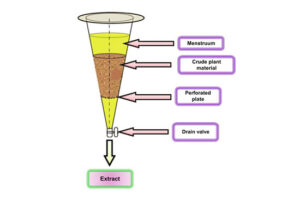
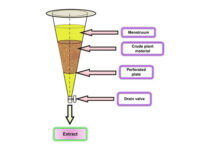
Percolation method
The percolation method uses a device called a percolator, which is a conical container. In this method, solvent extraction by drip method accompanies the active plant ingredients out of the percolator. The percolation method, like maceration, is suitable for substances that are sensitive to heat. The specialized unit of medicinal plants of Histogenotech is ready to provide services in the field of extraction with percolator for researchers.
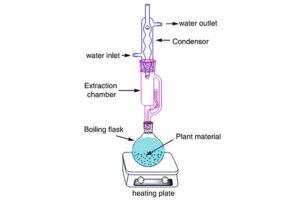
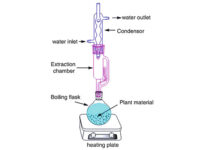
Soxhlet extraction
The Soxhlet extraction method is suitable for plant materials that are partially soluble in the selected solvent and for plant materials with insoluble impurities. However, this method is not suitable for heat sensitive plants. Histogenotech knowledge base Company with specialized staff and equipment is ready to provide services related to Soxhlet extraction
Microwave extraction
Microwave method is one of the advanced extraction methods in the preparation of medicinal products. This technique uses the mechanism of bipolar rotation and ion transfer by displacing charged ions in solvents and drugs. This method is suitable for extracting flavonoids. The use of non-polar solvents is not common in this method. With more than a decade of experience in the field of medicinal plants, Histogenotech is also ready to provide microwave services.
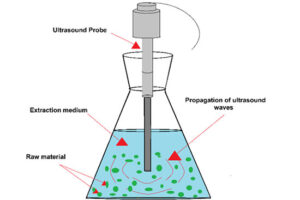
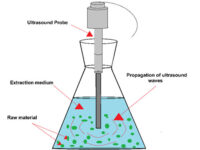
Extraction by ultrasonic method
This process involves the use of high-frequency sound energy (over 20 kHz) to disrupt plant cells and increase drug levels for solvent penetration. As a result, secondary metabolites are released. This method can be used for separation with the highest level. The Medicinal Plants unit of Histogenotech is ready to serve researchers in this field by using equipped devices.
Production of metal nanoparticles
Production of metal nanoparticles
Metals such as silver, gold, zinc, etc. are used to make nanoparticles. These particles have received much attention in nanotechnology due to their anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial effects. These particles are conductive in the human body due to their unique electrical and magnetic properties. Histogenotech nanotechnology unit is ready to provide services to researchers in the field of metal nanoparticles by using expert staffs and also using modern methods of synthesis and study of these particles.
Production of polymer nanoparticles
Production of polymer nanoparticles
Polymer nanoparticles (hydrogels) are three-dimensional polymer networks used to encapsulate and transport different factors like drugs, growth factors, and large molecules.To date, the Histogenotech Knowledge Base institute has developed more than 20 different projects in the field of metal nanoparticle synthesis and is still ready to provide polymer nanoparticle synthesis services (chitosan and liposomal).
Production of nano-emulsions
Production of nano-emulsions
Nano-emulsions are nano-sized structures that result from the integration of two non-integral phases such as water (W) and oil (O). The use of nano-emulsions is increasing in different industries such as pharmaceutical, cosmetic and food due to their greater stability and physical and chemical properties. Using the latest published methods and relying on the potential of its specialists, the Histogenotech nanotechnology department provides nano-emulsion synthesis services to researchers.
Production of plant essential oils
Essential oils (essential oils) are one of the most important active ingredients in medicinal plants. These substances are present in many parts of medicinal plants and contain different compounds such as hydrocarbons, alcohols, ketones, aldehydes, ethers, esters, which have many biological effects and activities. Histogenotech knowledge-based institute with equipped semi-industrial and industrial lines, is ready to provide services in the field of extraction different substances from medicinal plants.
Production of herbal medicine oils
Herbal medicine oils are fatty acids that are extracted from different parts of the plant, such as seeds. Like animal fats, they are rich in triglyceride fatty acids and, unlike essential oils, have a sour smell and taste when left in the environment. These compounds are very important in many different industries, especially food and cosmetics. Histogenotech is ready to provide services in the field of Herbal medicine oil extraction by distillation and cold pressing, on a semi-industrial and industrial scale.


You may find the answer to your question
Frequently Asked Questions by Customers
In biological studies, it is often better to use methods that do not use heat to investigate the effects of active substances on biological processes. Because the active ingredients are sensitive to temperatures above 70-60 degrees Celsius. The proposed method for extraction in biological studies is the maceration method.
Plants are classified based on essential oils. Some, such as sage, are low in essential oils and some plants, such as rosemary, are high in essential oils. In addition, environmental conditions and geographical area of cultivation also affect the amount of volatile fatty acids (essential oils) of the plant. In general, there is no rule on how much essential oil is obtained from one kilo of plant and there is a need for trial and examination. Of course, the Histogenotech has performed this examination for many plants, which makes it easier for clients to have a pure essential oils.
Essential oils (essential oils) are one of the most important active ingredients in medicinal plants. These substances are present in many parts of various medicinal plants. Essential oils evaporate if exposed to normal temperatures. Hence they are called volatile oils and the specific odor of some plants is related to this group of compounds. Essential oils differ from fixed oils in some chemical and physical properties, the most important of which are: 1. Essential oils can be distilled and therefore can be easily extracted through distillation methods. 2. The chemical structure of essential oils is not made from glycerin esters and fatty acids, unlike fixed oils. 3. Unlike essential oils, essential oils do not spoil or turn sour. Instead, they will form oxidized and resin in the presence of air and light.
Different solvents (water, ethanol, methanol, water-alcohol combination, hexane, etc.) can be used for extraction. But the choice of solvent depends on the properties of the active ingredients. For example, polarity, solubility and many other factors should be considered for solvent.
There are a variety of methods for concentrating plant extracts. But the easiest way is to pour a certain amount of extract (for example, 5 ml) in a pre-weighed plate. Place the plate in a high temperature oven and weigh it again after the liquid is completely dry. With this method, it is easy to find out the concentration and amount of extract in the liquid.
Yes, the extraction of certain plant active ingredients can be done from plant extracts and requires special equipment such as chromatography. For example, the HPLC method, which is a chromatographic method, can be used to both identify and determine the presence of an active substance and to extract that active substance.
Like essential oils, the amount of active ingredients in plants varies. In general, it can be said that three different factors affect the amount of extract. 1. Differences in cultivated geographic conditions like light conditions and other environmental conditions. 2. Differences in solvent used for extraction. 3. The plant organ that is selected for extraction (for example, the leaves of plants are a richer area than the seed for extraction).
The extract should be clear, free of foreign particles, without turbidity and sediment. The color of the extract should be appropriate for the plant and the ingredients in it. The smell of the extract should be similar to the smell of the plant. However, some extracts are less aromatic due to the use of glycolic solvents, especially hydro-glycolic extracts. Although some extracts contain antibacterial agents, laboratory bacteriological tests are sometimes needed to evaluate the contamination of extract.