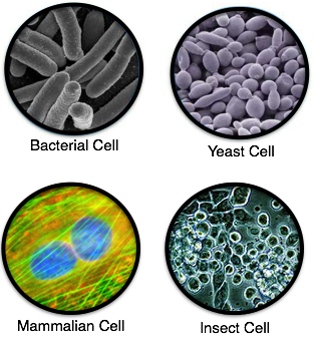
Different types of expression systems of recombinant proteins
introduction
Different types of expression systems of recombinant proteins
Proteins, as one of the essential macromolecules in the biological world, play a significant role in the metabolic and catabolic systems of organisms that are involved in critical cellular processes such as cell signaling, cell adhesion, immune responses, and cell division. Nowadays, the commercial production of proteins in enzymatic, agricultural, and pharmaceutical industries is increasingly expanding based on protein and genetic engineering; so that the products in these industries can cover a significant part of the needs of communities. Systems established for the expression of the recombinant proteins are a combination of an expressing vector, cloned DNA, and a host for the vector. These factors stimulate the external gene to be activated in a host cell and produce the desired protein. The design of an optimum
system for the production of the recombinant proteins include several crucial steps as follows:
- Choosing the host strain that has the ability to correctly folding and post-translational changes
- Choosing the right carrier with a strong promoter and a selective marker
- Conjugate a tag to the gene to make protein purification
- Selection of signal sequences to conduct the recombinant protein into intracellular or extracellular space
- Prevention of product degradation by proteinases
- Optimize codon
- Optimization of growth and induction process parameters (pH, Temperature, O2 transfer)
Host cells used for the expression of protein are very different. Each of these expression systems has its advantages and disadvantages. Prokaryotic systems include gram-negative bacteria, and eukaryotic systems consist of new strains of yeast, stringy fungi, as well as systems based on plants and insects that have made significant advances in recent years. Laboratory systems have been established that are cell-free and able to translate the target protein. The quality of the protein, performance, speed, and production efficiency are the most significant factors when the perfect expression system is selected for the production of recombinant proteins. Each expression system has a number of strengths and weaknesses that can be divided into features in terms of cost, speed, ability to glycosylation, and protein folding. Bacteria are the fastest and cheapest expression system for the expression of recombinant proteins; however, they are unable to glycosylate the expressed proteins or fold them properly. Mammalian cells perform the glycosylation and folding of proteins, but the maintenance of these types of cells would be expensive. Therefore, to determine which system of expression for a recombinant protein should be applied would be dependent on the protein and its inherent properties.
Related posts: Production of recombinant proteins by yeasts – Recombinant protein expression in filamentous fungi