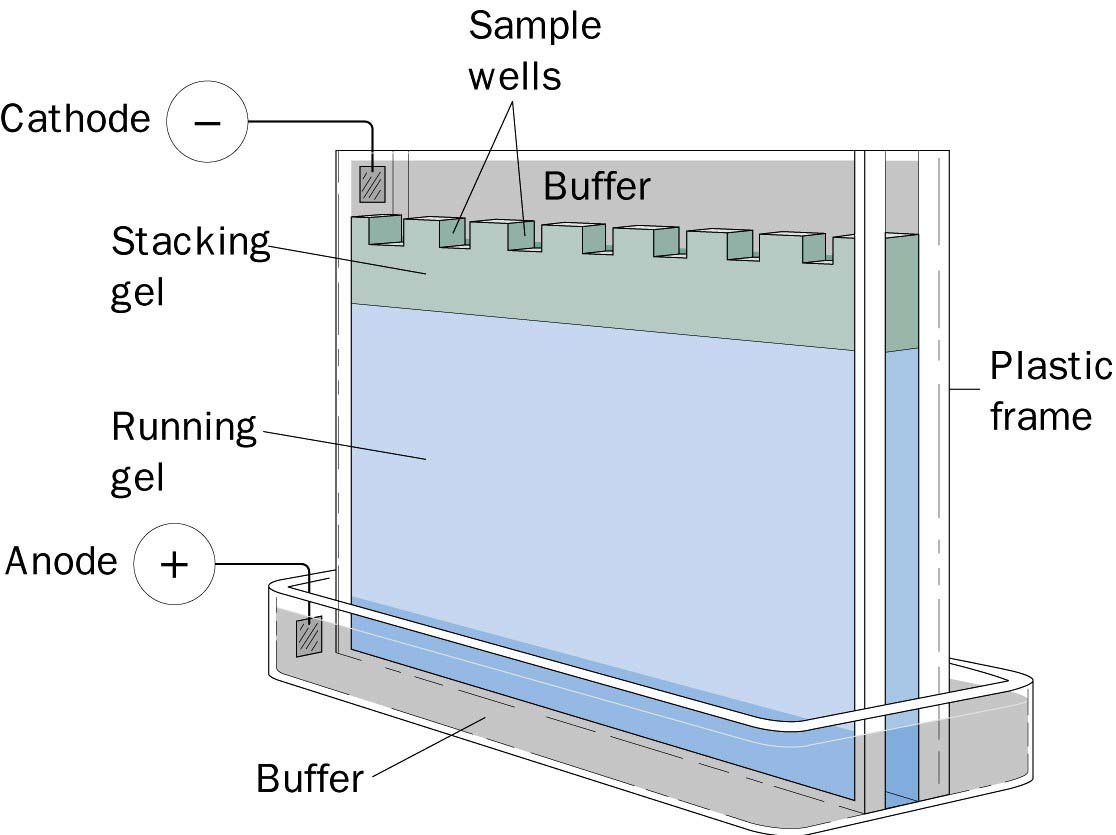
Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis in western blot technique

Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis in western blot technique
Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis is used to isolate proteins in sizes from 5 to 200 kDa due to the presence of pores of the same size and shape. The pore sizes are controlled by the concentration of acrylamide and the bis- acrylamide powder used in the gel. The percentage of the selected gel depends on the protein to be detected.
In general, the protein/gel ratio is as follows :
- If the protein is less than 10 kilodaltons, the gel is used at 15%
- If the protein is less than 10-30 kilodaltons, the gel is used at 12%
- If the protein is less than 30-100 kilodaltons, the gel is used at 10%
- If the protein is less than 100-200 kilodaltons, the gel is used at 8%
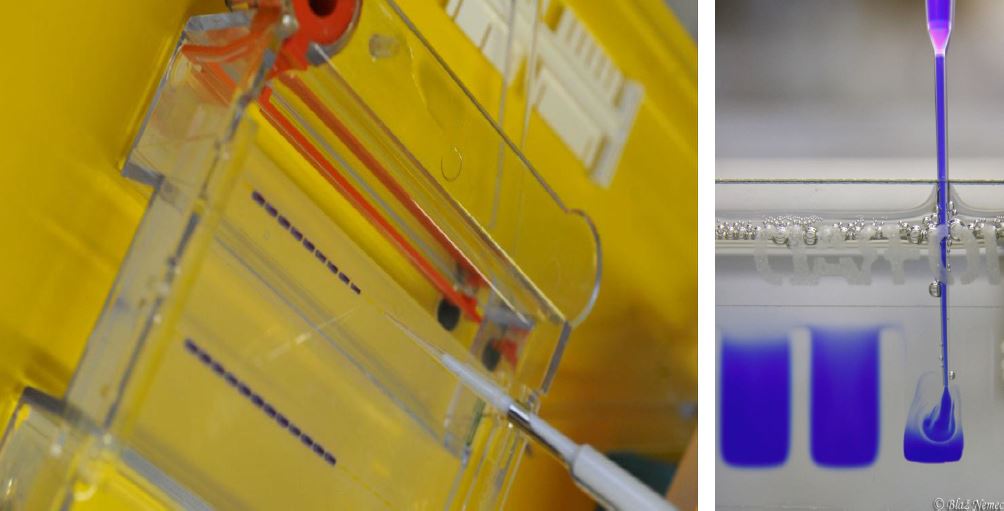
The polyacrylamide gel consists of two sections. The lower section is the separating gel, and the upper section is the stacking gel. The wells locate on stacking gel, and samples and ladders are loads on it. The concentration of this gel is typically 4%, and after removal of proteins in the electrophoresis apparatus, it is separated from the gel. The separating gel is the place where proteins run.
Related posts: protein expression assay by western blot in tissue or cell – Types of materials and equipment required in Western blot techniques