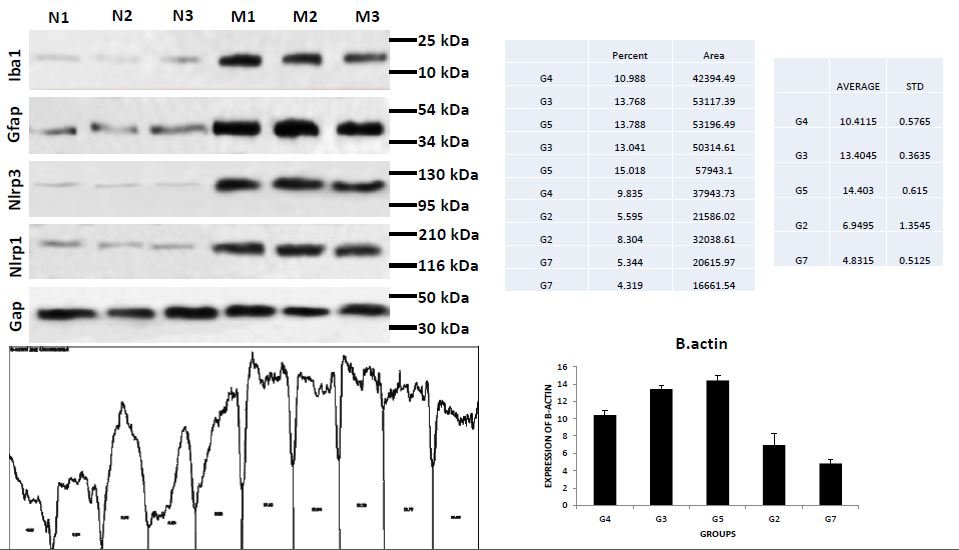
The interpretation of paper and unusual bands in Western Blot
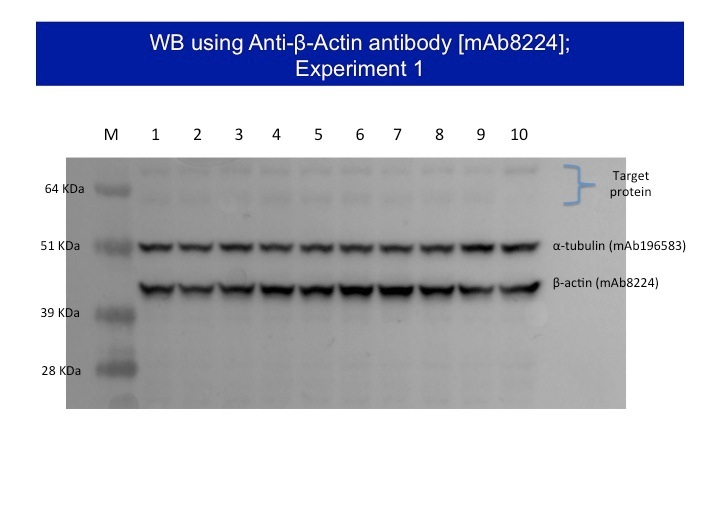
The interpretation of paper and unusual bands in Western Blot
Although Western blotting is a relatively simple technique, there may be problems during the work, which can lead to unexpected results, including:
- Unusual and unexpected bands
- Lack of band
- Band or weak signals
- A lot of background on paper
- Uneven points on paper
- Unusual band
Unusual bands
- These bands can be come by protease damage, which leads to the creation of bands in unexpected situations.
- To overcome this problem, it’s best to use a fresh sample that is kept on ice or change the antibody. If the protein bands are higher than the desired level, warming the sample can help break the quadruple protein structure.
- Fading bands are often created due to high voltages or air bubbles in the power flow. In this case, it must be ensured that the gel is run at low voltage, and the western sandwich is properly prepared.
- Changing the running buffer can also help resolve this problem.
No band formation
- Failure to form the band may be due to several reasons that are relevant to the antibody, antigen, or using the buffer.
- If the inappropriate antibody is used (whether primary or secondary), no bands will be shown; also, the antibody concentration should be appropriate.
- if it is too low, the signal may not be visible. It should be kept in mind that some antibodies are not usable for the Western.
- Another reason may be a low concentration or the absence of an antigen; in this case, another source can be used to confirm the problem of the sample or other elements such as antibodies.
- Long wash can also reduce the signal. Buffers can also help with this problem.
- It should be noted that buffers such as buffer transfer, TBS, and running buffer to be all fresh and non-contaminated. If buffers are contaminated with sodium alginate, they can disable HRP.
- Another reason is the use of non-fat powdered milk that can cover the antigen. In this case, BSA can be used as a blocker buffer or reduce the use of milk.
Western & Uneven bands
These bands can be created as a result of the rapid movement of proteins in the gel.
High background
• It is often created with excessive concentration of An antibody that can be attached to PVDF paper.
• Another problem can be the rinse buffer, which may be very old. Increasing the rinse time can help reduce the background.
• Excessive exposure to antibodies can lead to this problem.
Rough and uneven points on paper
- These points are caused by the inappropriate transfer. If air bubbles between gels and paper are trapped during transfer, they appear on film or paper.
- It is important to use a shaker for all stages of incubation. Repeated washing is very important to background be washed off.
- This problem may also be due to antibodies associated with blocking agents. In this case, another blocking buffer should be tested. Blacking buffer filtering can also help to remove some contaminants.
Related posts: Types of materials and equipment required in Western blot techniques – Different methods for identifying and interpreting incomplete bands of western blot techniques