Removal of genomic DNA contamination during total RNA extraction
Removal of genomic DNA contamination during total RNA extraction
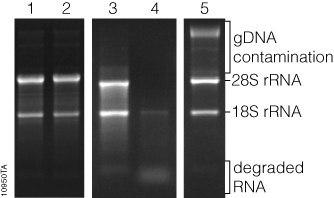
To reduce phenolic contamination, ethanol 75% wash can be repeated until the sample is clean. It has been shown that phenolic contamination does not suffer from downstream programs and can be neglected.
Generally, the extracted RNA in the previous step is contaminated with genomic DNA that interferes with qPCR experiments. To eliminate it, there are several methods, including DNase treatment of extracted RNA samples.
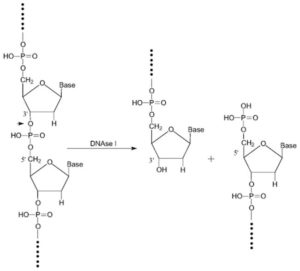
In using the DNase enzyme to eliminate DNA, it should be noted that the enzyme’s neutralization should be performed appropriately with EDTA because high-temperature magnesium has the potential to destroy RNA.
There are several methods in addition to DNase to eliminate DNA, such as DNA Removal Columns, the use of lithium chloride (lithium chloride is not recommended for miRNA) and magnetic beads (m-beads).
Also, with the design primers mainly from a specified exon-exon junction for RNA, the effect of contamination with DNA can be neutralized.
One of the ways to detect DNA contamination in extracted RNA is to use gel electrophoresis, which, due to its heaviness, lies in the upper portion of the gel and can be distinguished from RNA and cDNA.
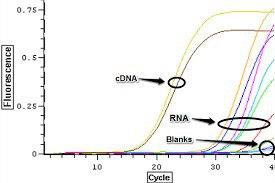
Real-Time pcr is another method to detect DNA contamination, which, the RNA sample along with the cDNA specimens replicate for the desired gene, and the proliferation of this product indicates the contamination of the sample with DNA.
Related posts: Quantitative analysis of the extracted RNA cell or tissue with spectrophotometer – cDNA synthesis from RNA extraction from tissue and cell