Cell cycle processes and separation
Cell separation
Cell cycle processes and separation
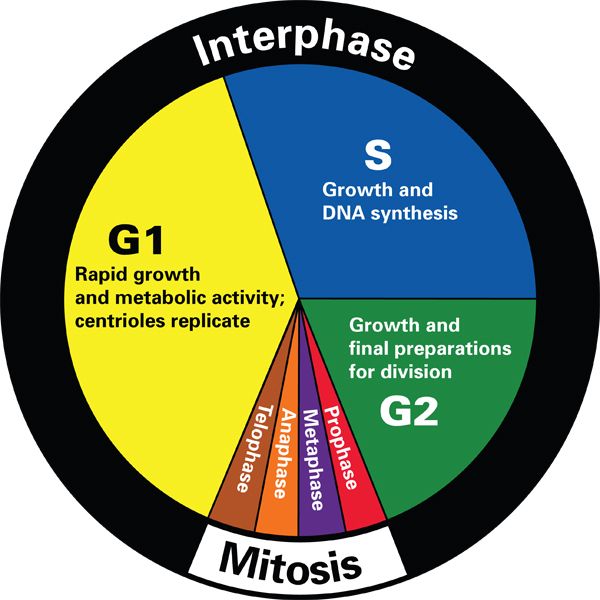
The cell cycle consists of four phases: G1, synthesis, G2, and mitosis.
The cell cycle processes are regulated by the interaction of cyclins with their dependent kinas. The cell cycle is stopped by inhibitors such as RB and P53.
G1 phase
At the G1 phase, cells can be developed to synthesize DNA and so other cell division, or the cells can enter reversible (quiescent) or irreversible (senescent and differentiated) G0 states from the G1 phase of the cell cycle, so that at this stage, the existence of specific regulatory points can determine the cell’s destiny for differentiation Or enter into the cell cycle.
G2 & synthesis phases
At the G2 and S phase, the presence of control points confirms the integrity of DNA. In the event of a defect, the cell cycle will go towards the repair or programmed cell death. Apoptosis is detectable via various laboratory techniques.
Distinction
With increasing of proliferation, the expression of differentiation markers is limited, thus in order to induce differentiation in high cell density, the interaction increasing between cell-cell, cell-matrix and the presence of differentiation markers, inhibits cell proliferation and induces differentiation.
Tips on separating cells from each other :
Proteases cause the cells to separate from each other as well as from the tissue, and cells do not stick in single-layer culture, which is due to digestion of the extracellular matrix.
Epithelial cells are resistant to detachment due to tight joints.
In mesenchymal cells, because the connections are through cell matrices, thus they are easily separable. Endothelial cells express tight connections, and they hardly separate. In each of these cases, matrix proteins must be generated before binding, or they must be supported by a matrix-coated substrate.
Related posts: Effective factors of medium on cultured cells – equipment and Different cell culture techniques